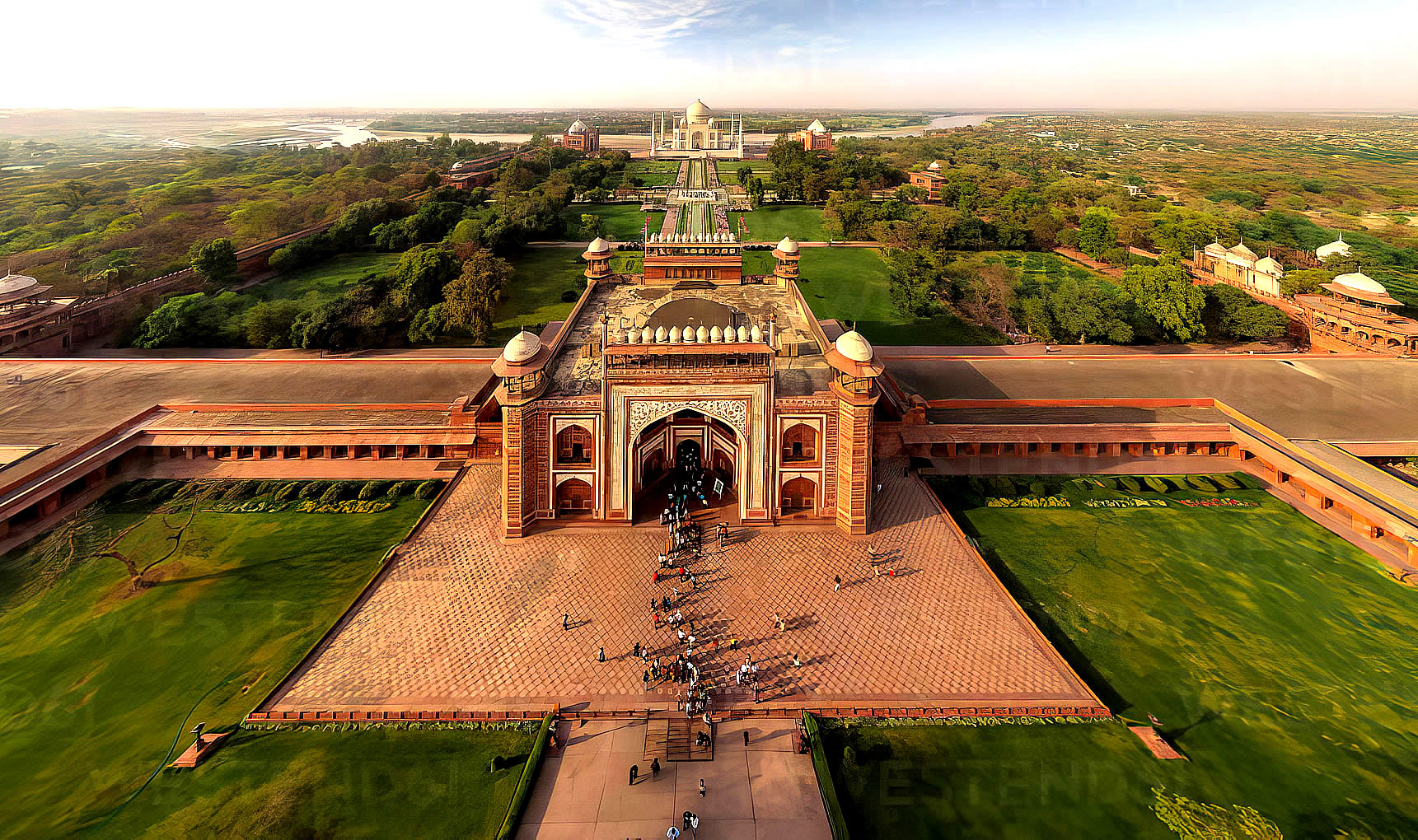
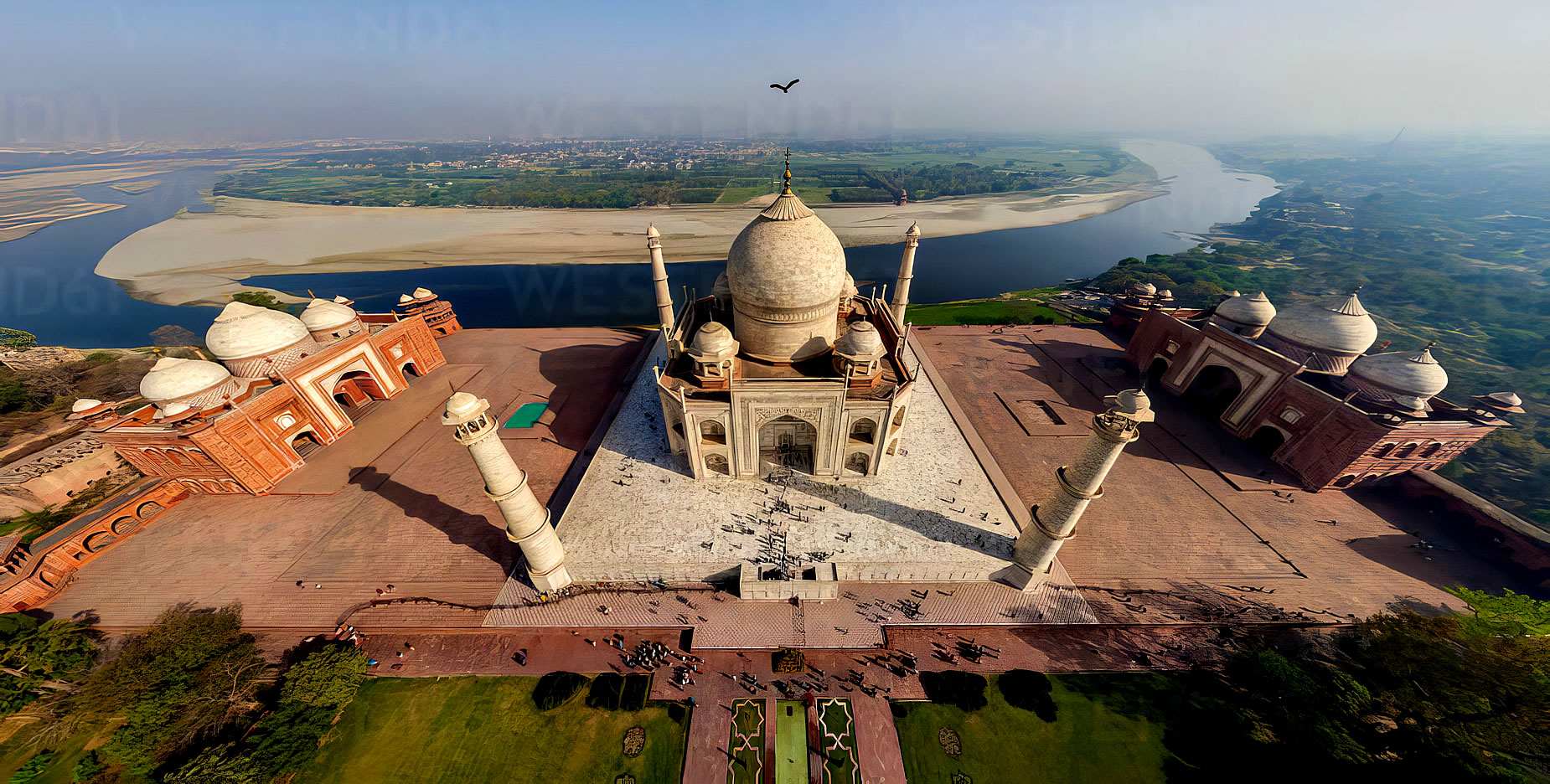
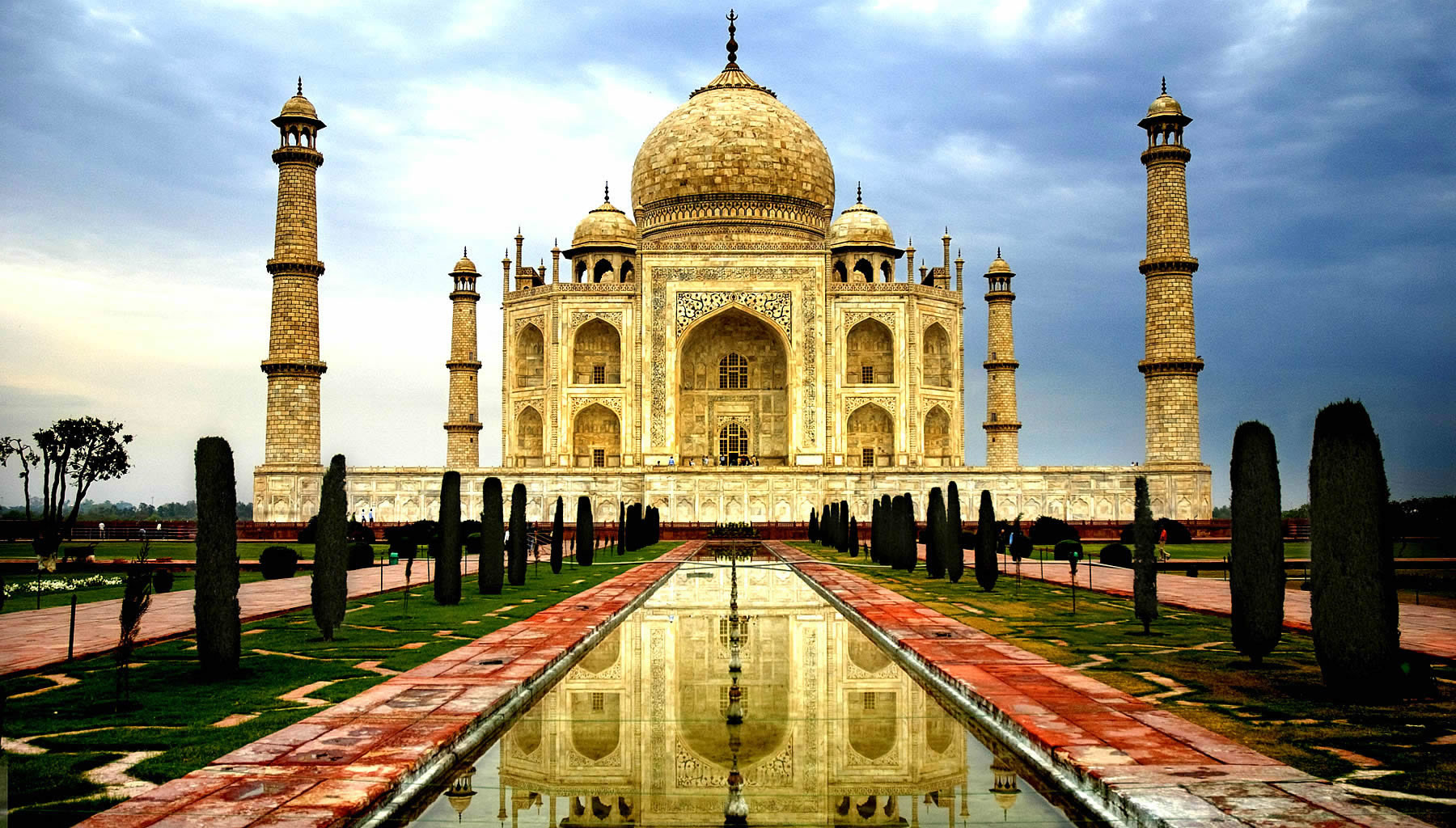
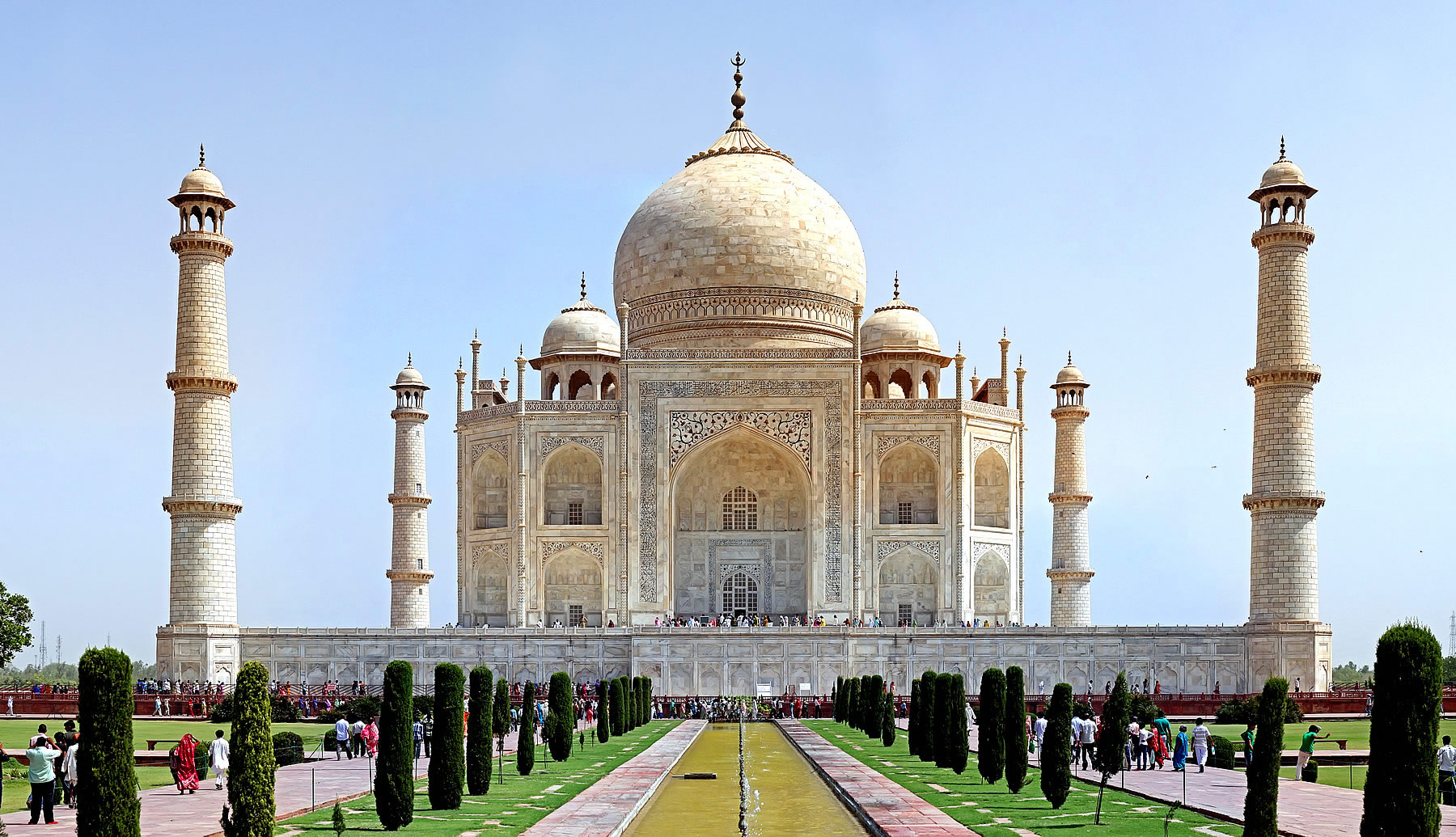
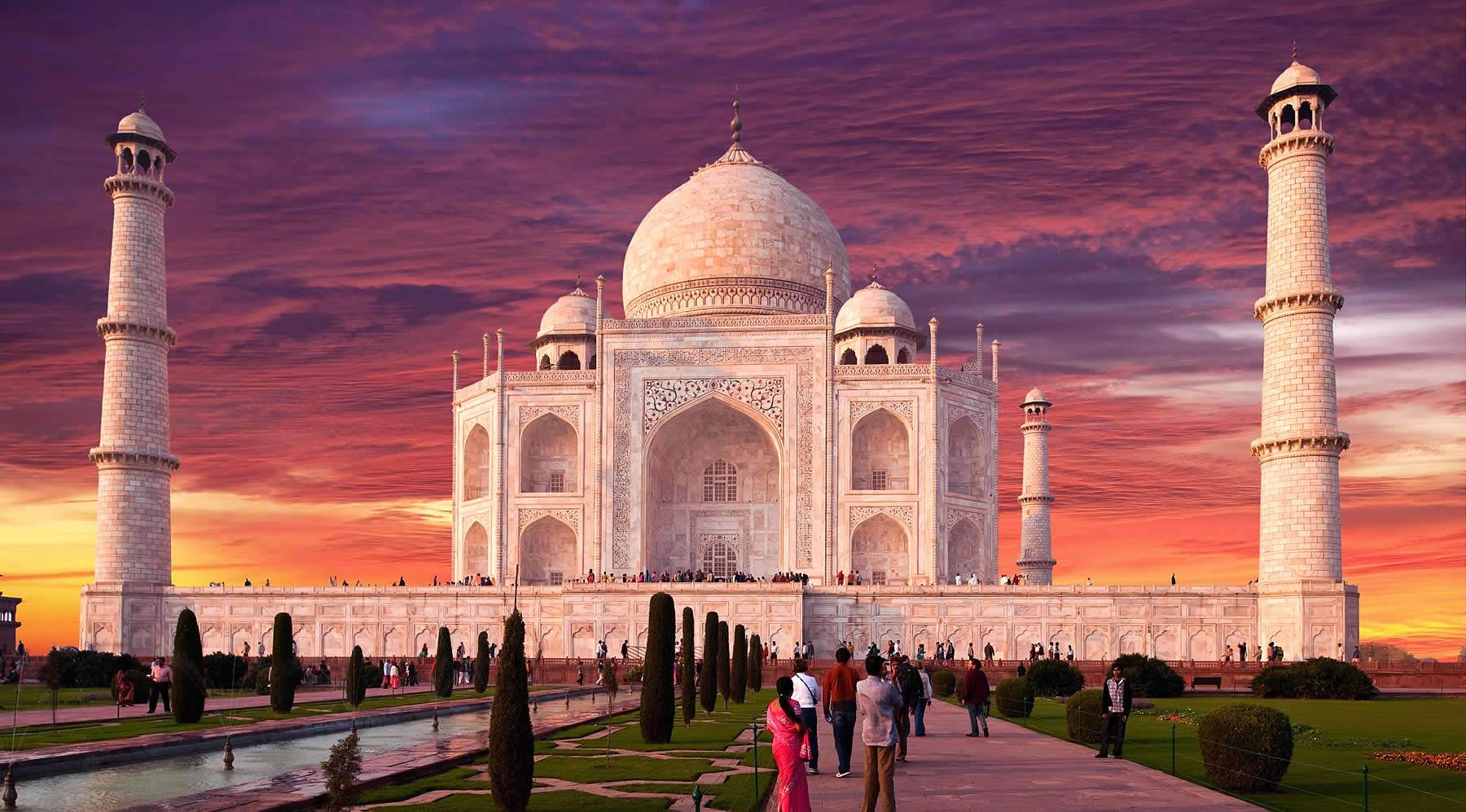
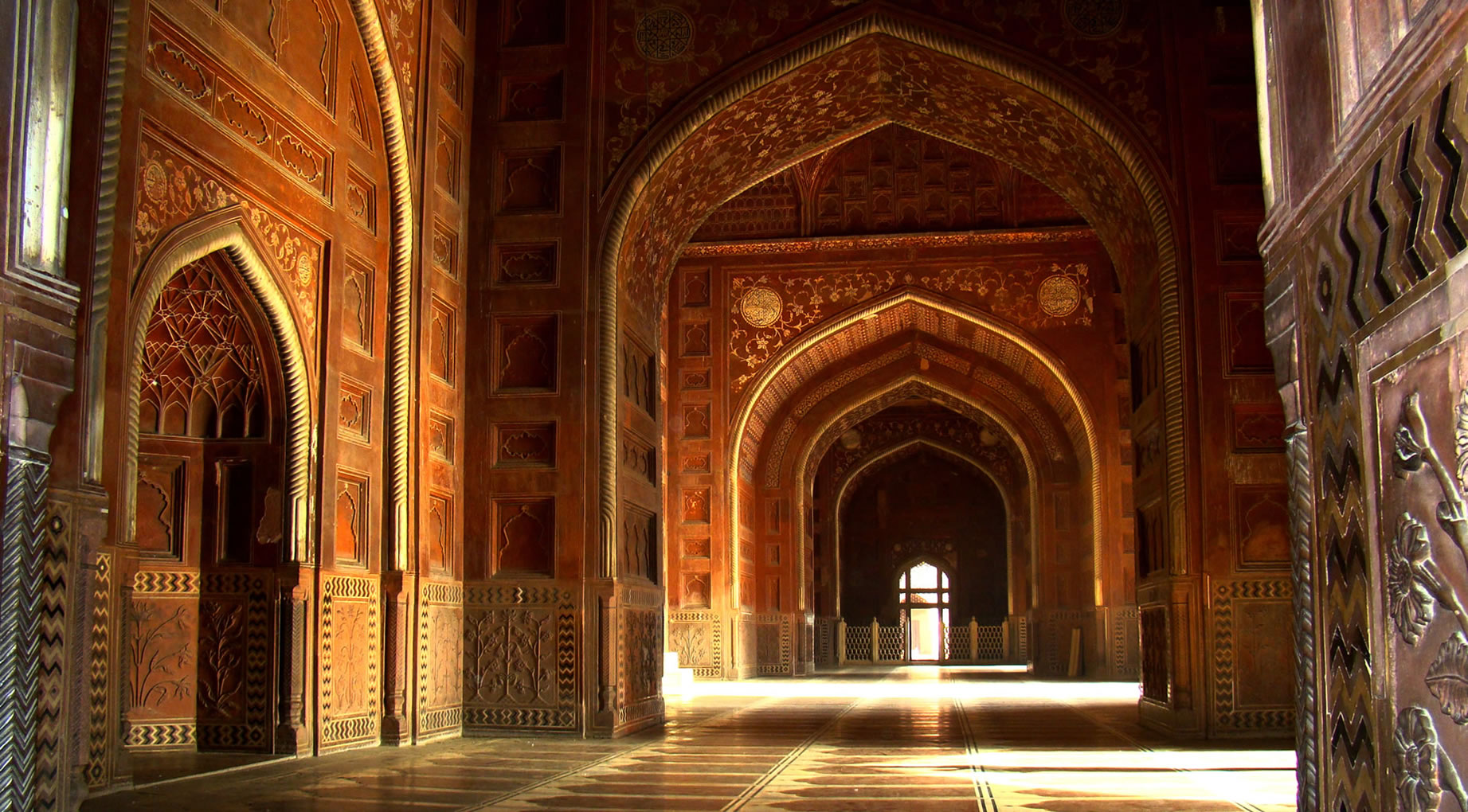
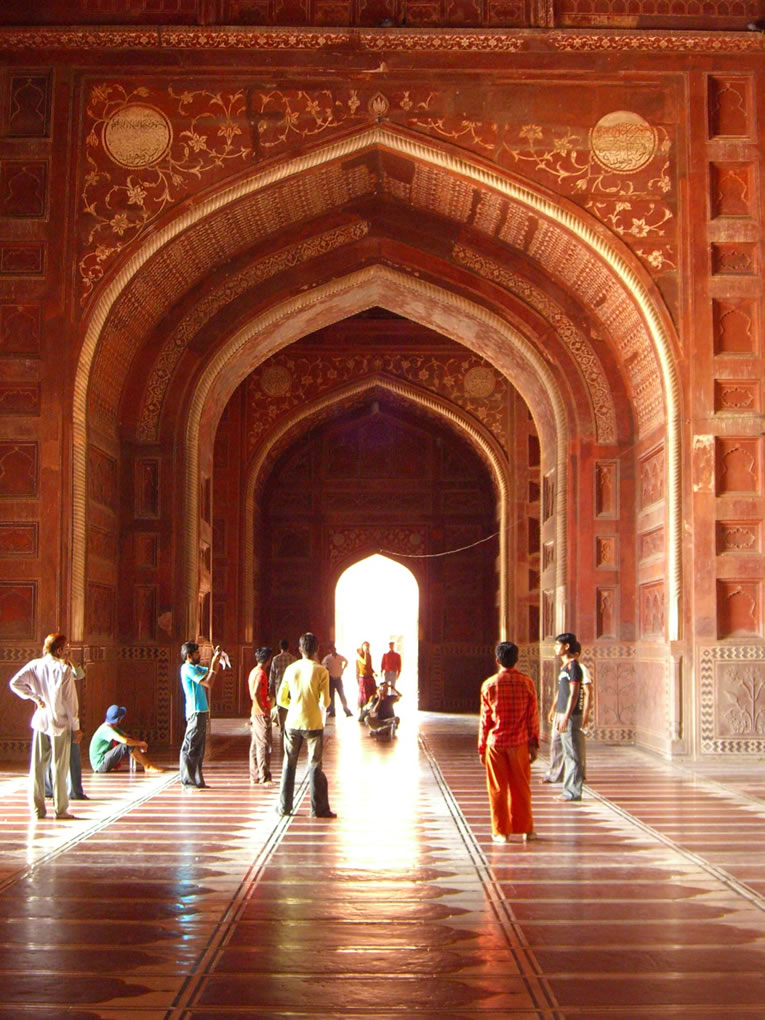
| The Taj Mahal (/ˌtɑːdʒ məˈhɑːl, ˌtɑːʒ-/; lit. 'Crown of the Palace') is an Islamic ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in the Indian city of Agra. It was commissioned in 1631 by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan (r. 1628–1658) to house the tomb of his favourite wife, Mumtaz Mahal; it also houses the tomb of Shah Jahan himself. The tomb is the centrepiece of a 17-hectare (42-acre) complex, which includes a mosque and a guest house, and is set in formal gardens bounded on three sides by a crenellated wall.
Construction of the mausoleum was essentially completed in 1643, but work continued on other phases of the project for another 10 years. The Taj Mahal complex is believed to have been completed in its entirety in 1653 at a cost estimated at the time to be around ₹32 million, which in 2020 would be approximately ₹70 billion (about US $1 billion). The construction project employed some 20,000 artisans under the guidance of a board of architects led by Ustad Ahmad Lahauri, the emperor’s court architect. Various types of symbolism have been employed in the Taj to reflect natural beauty and divinity.
The Taj Mahal was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1983 for being "the jewel of Muslim art in India and one of the universally admired masterpieces of the world's heritage". It is regarded by many as the best example of Mughal architecture and a symbol of India's rich history. The Taj Mahal attracts more than 6 million visitors a year and in 2007, it was declared a winner of the New 7 Wonders of the World (2000–2007) initiative.
|
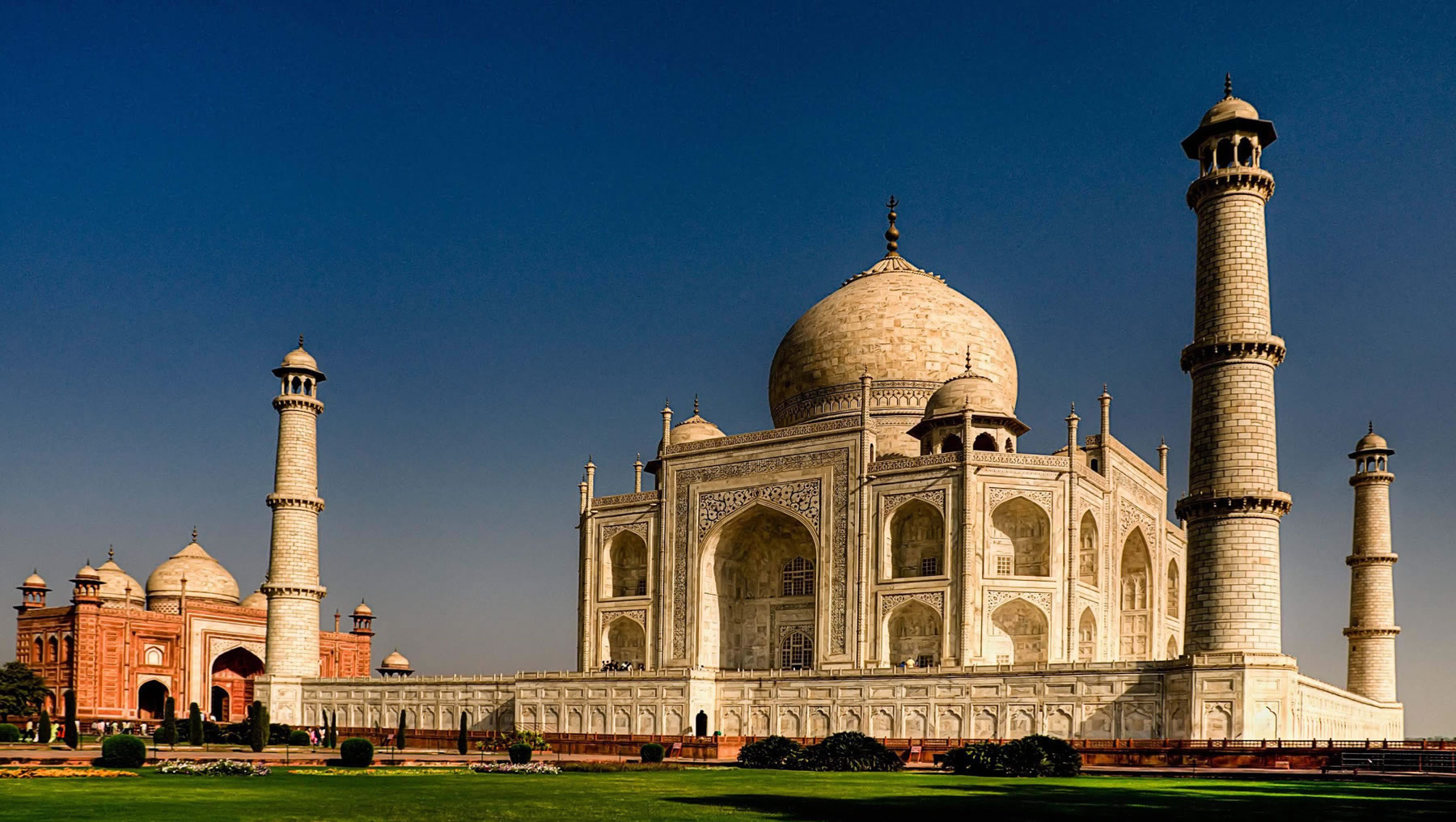
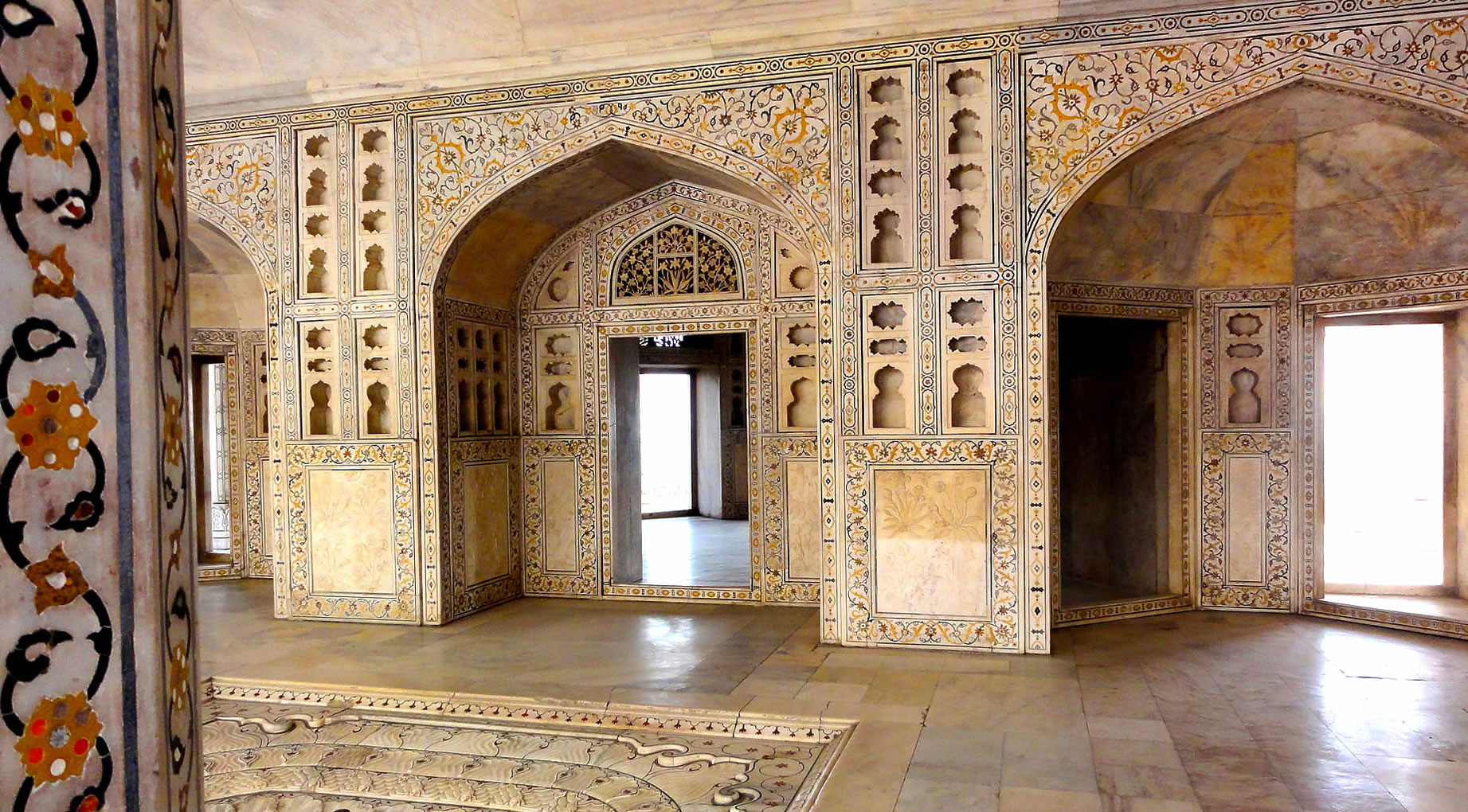
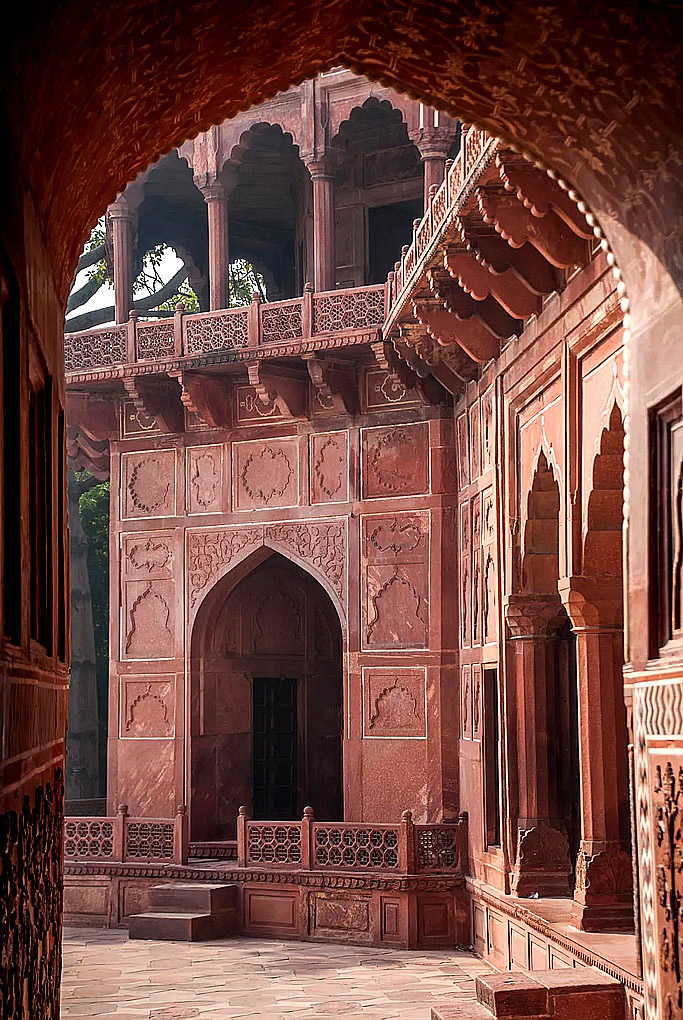
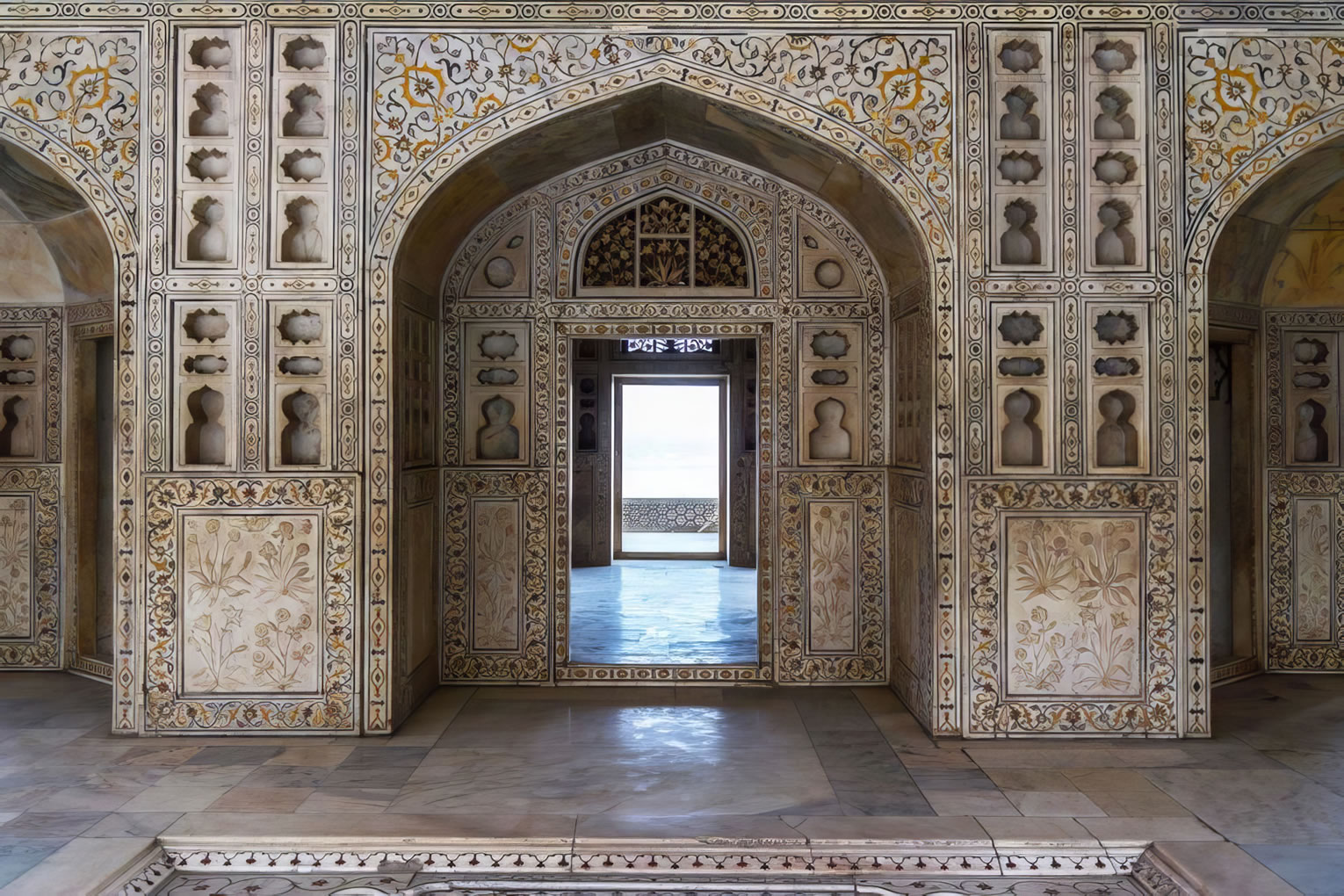
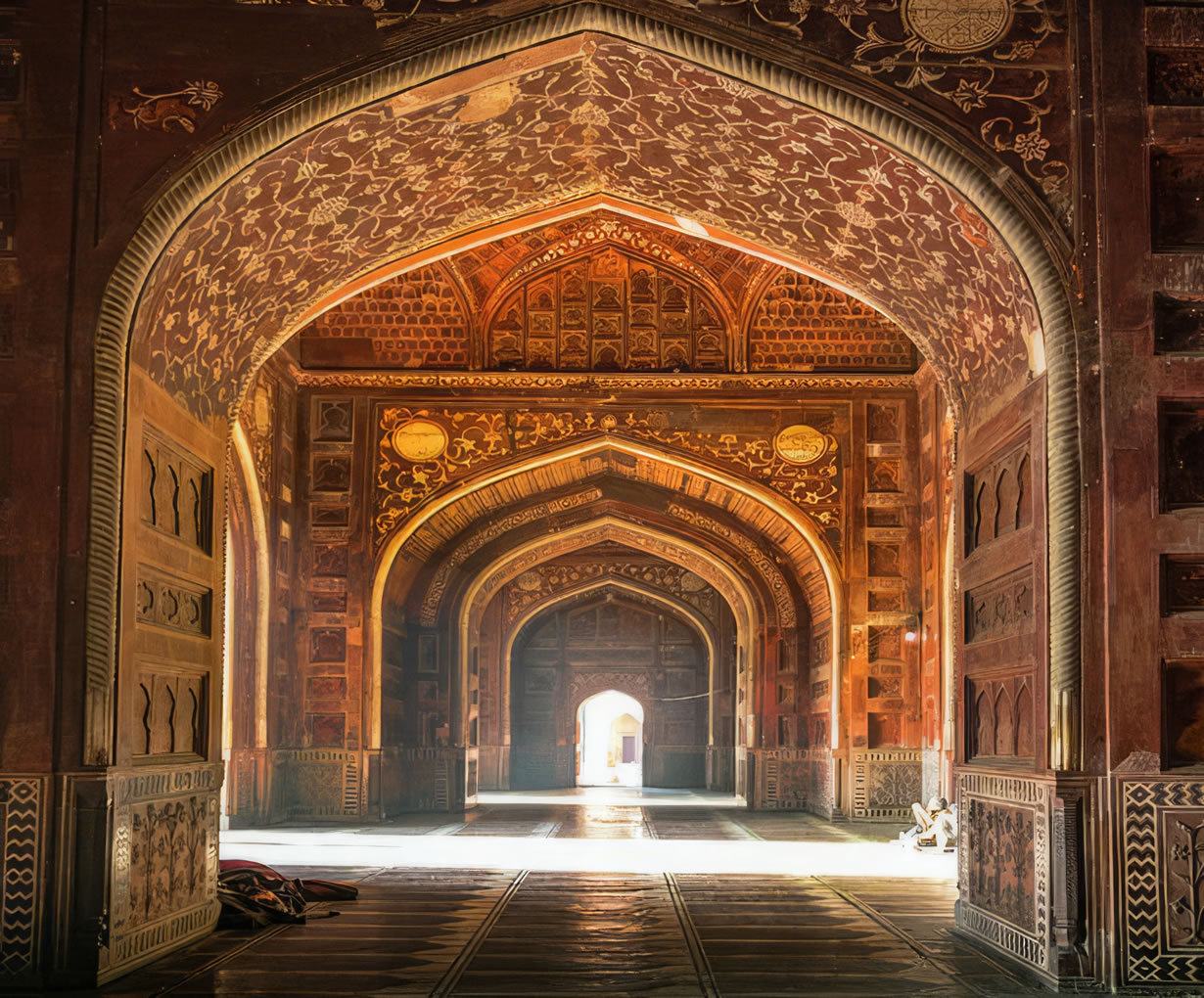
The Taj Mahal incorporates and expands on design traditions of Indo-Islamic and earlier Mughal architecture. Specific inspiration came from successful Timurid and Mughal buildings including the Gur-e Amir (the tomb of Timur, progenitor of the Mughal dynasty, in Samarkand), Humayun's Tomb which inspired the Charbagh gardens and hasht-behesht (architecture) plan of the site, Itmad-Ud-Daulah's Tomb (sometimes called the Baby Taj), and Shah Jahan's own Jama Masjid in Delhi. While earlier Mughal buildings were primarily constructed of red sandstone, Shah Jahan promoted the use of white marble inlaid with semi-precious stones. Buildings under his patronage reached new levels of refinement.
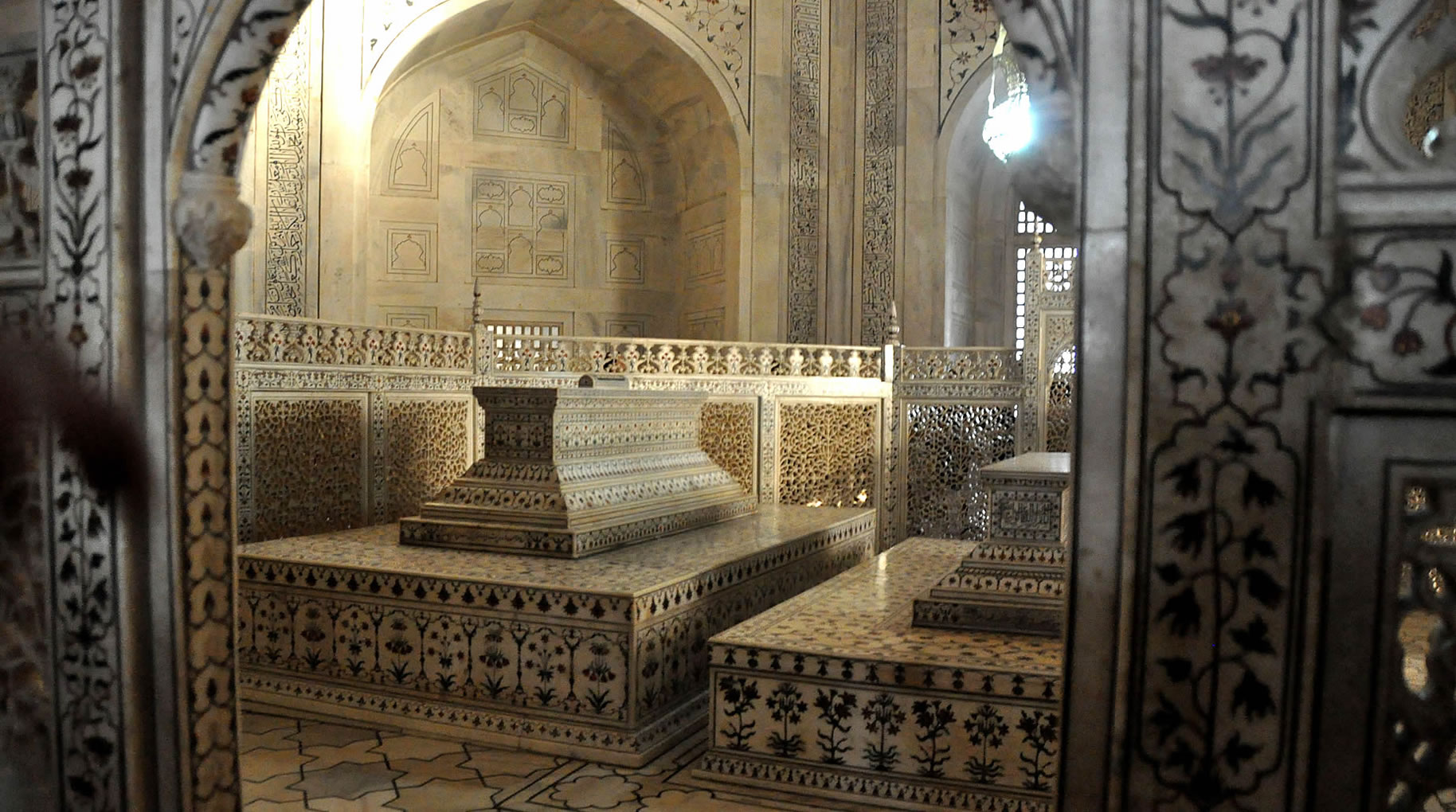
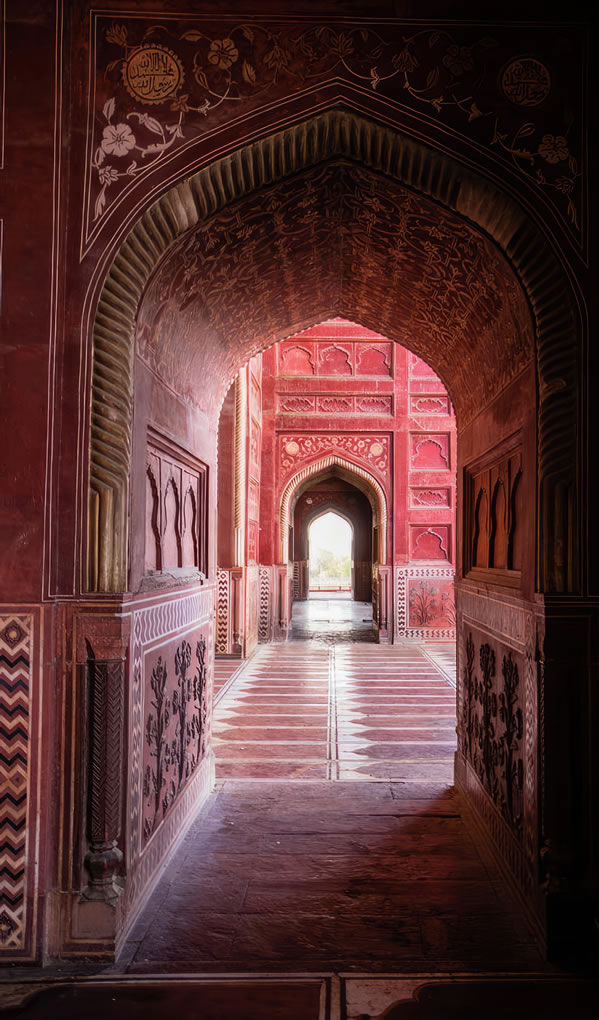
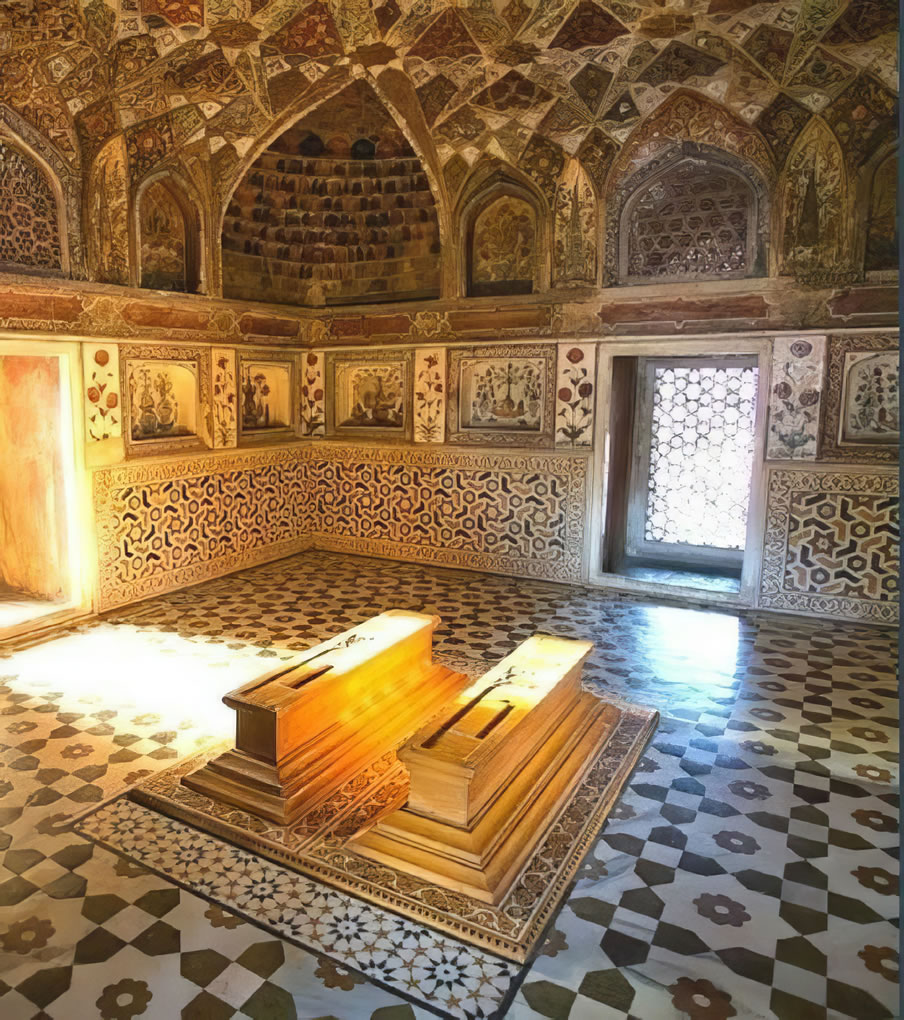
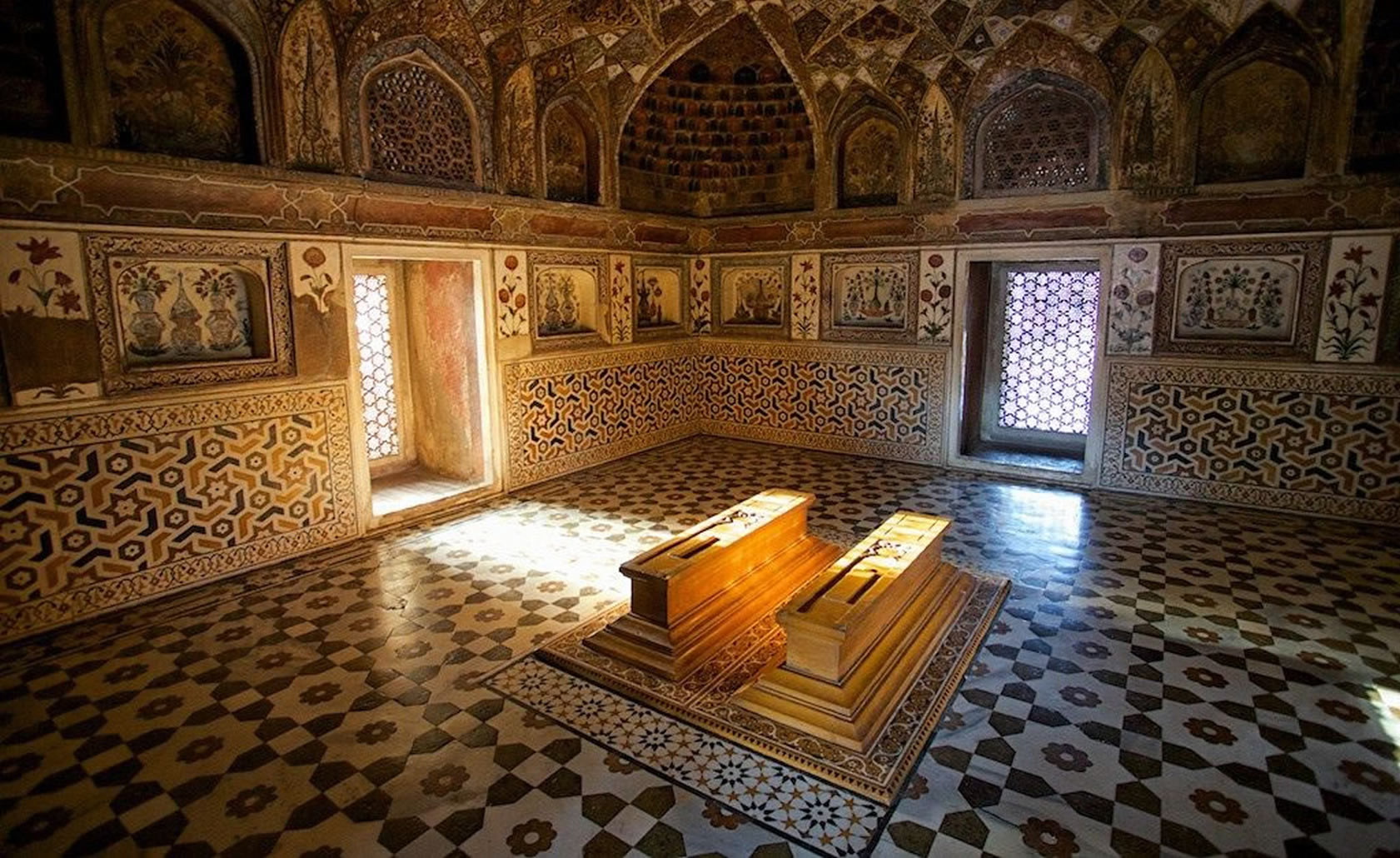
The tomb is the central focus of the entire complex of the Taj Mahal. It is a large, white marble structure standing on a square plinth and consists of a symmetrical building with an iwan (an arch-shaped doorway) topped by a large dome and finial. Like most Mughal tombs, the basic elements are Indo-Islamic in origin. The base structure is a large multi-chambered cube with chamfered corners forming an unequal eight-sided structure that is approximately 55 metres (180 ft) on each of the four long sides. Each side of the iwan is framed with a huge pishtaq or vaulted archway with two similarly shaped arched balconies stacked on either side. This motif of stacked pishtaqs is replicated on the chamfered corner areas, making the design completely symmetrical on all sides of the building. Four minarets frame the tomb, one at each corner of the plinth facing the chamfered corners. The main chamber houses the false sarcophagi of Mumtaz Mahal and Shah Jahan; the actual graves are at a lower level. |