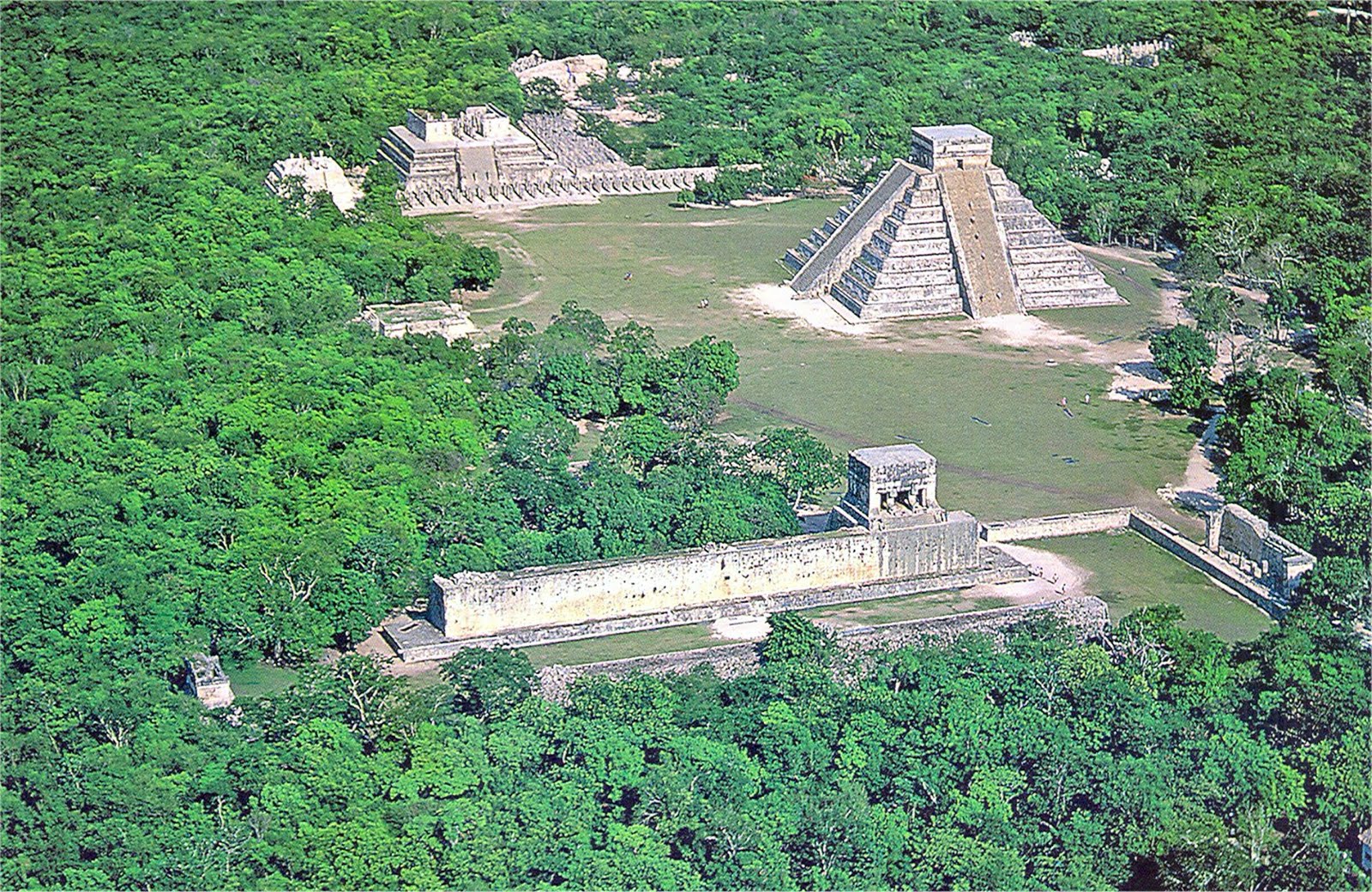
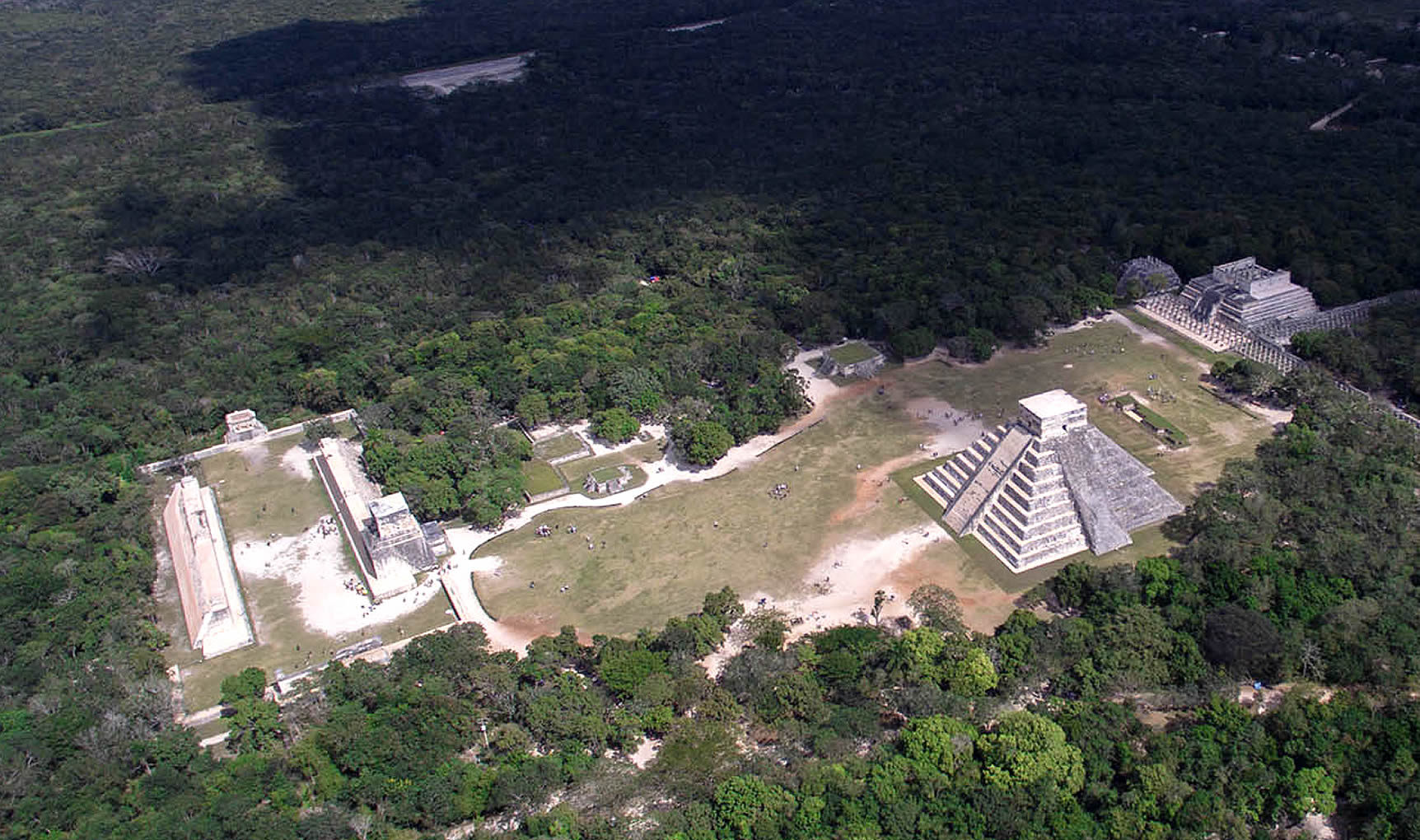
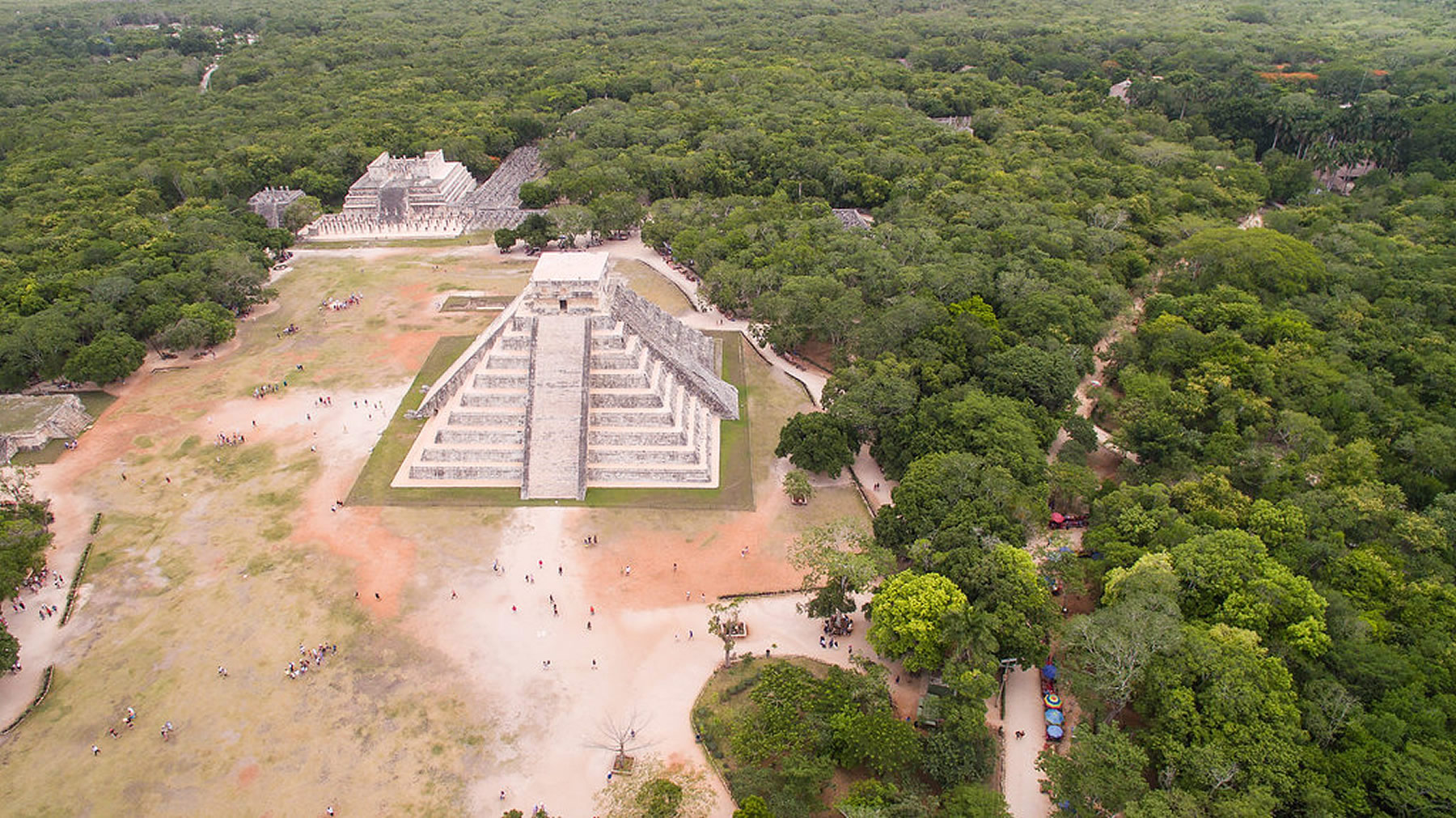
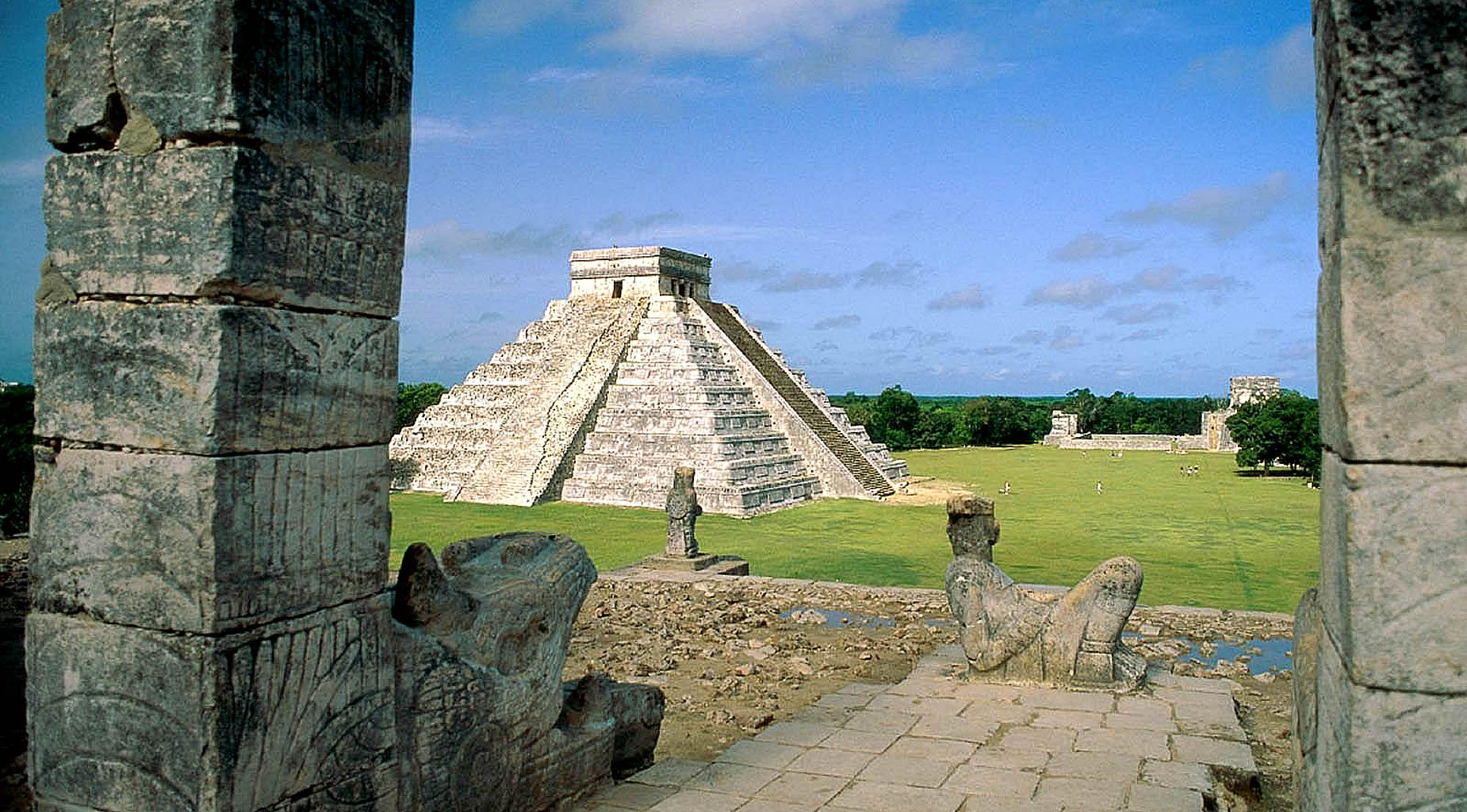
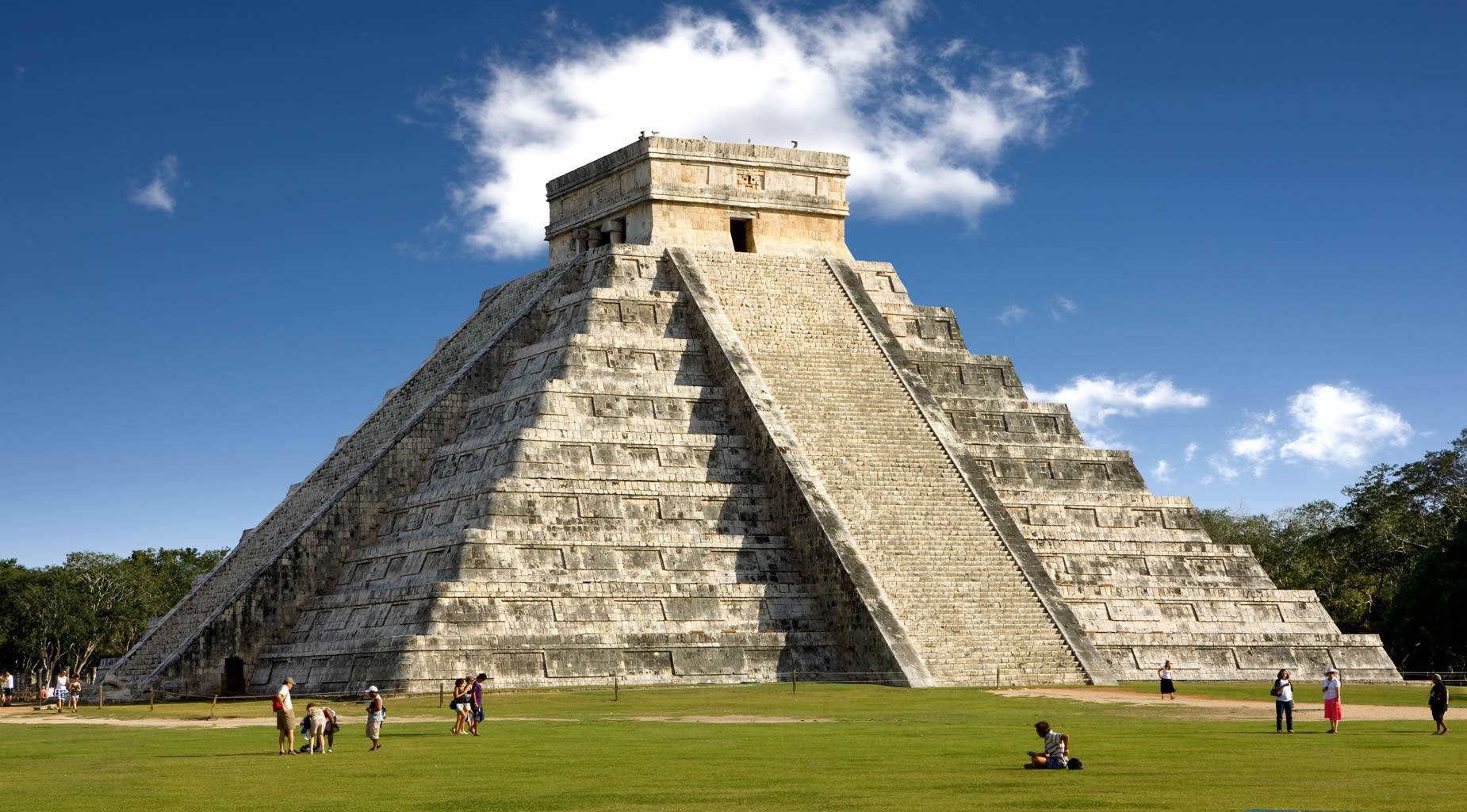
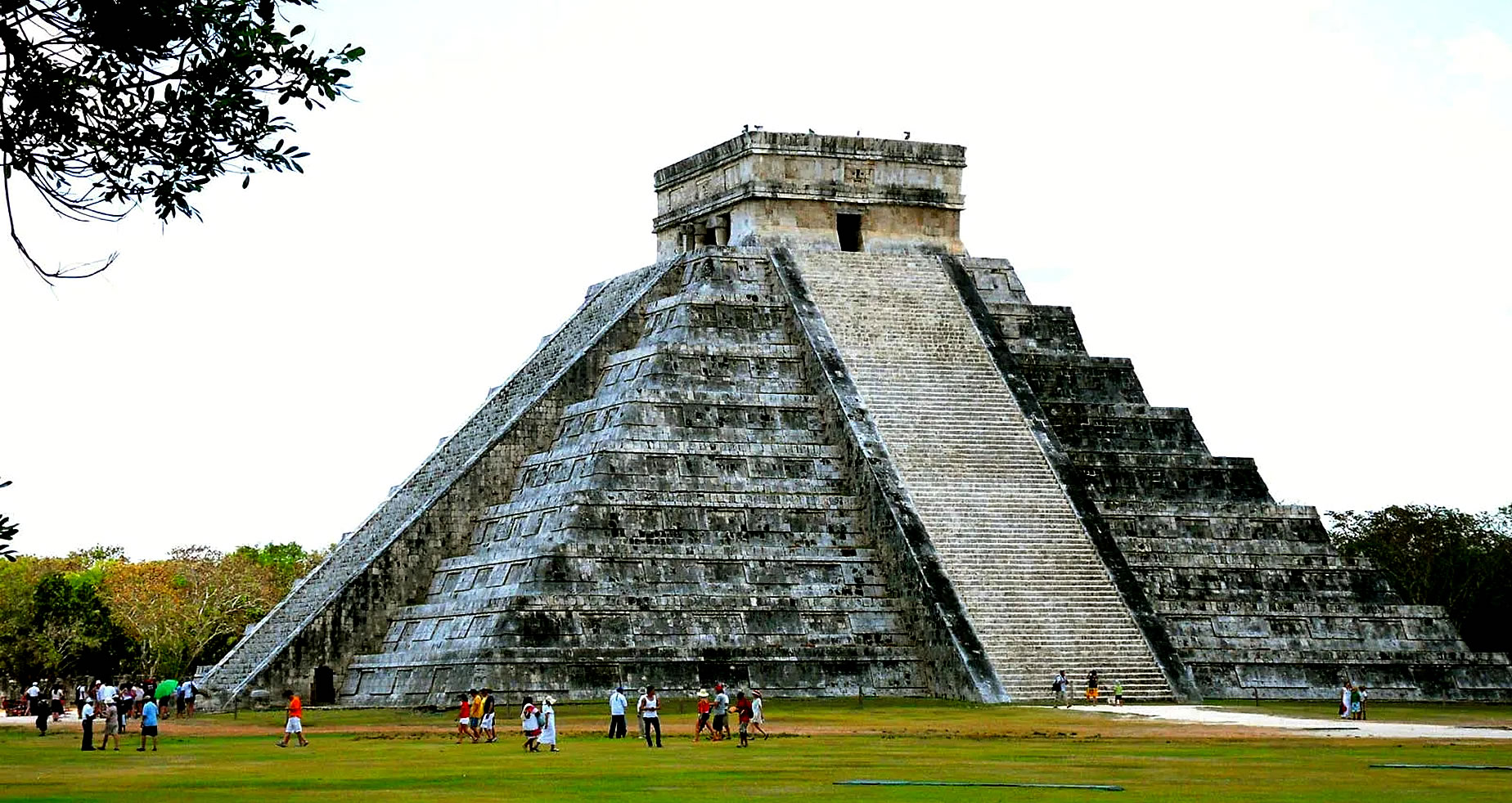
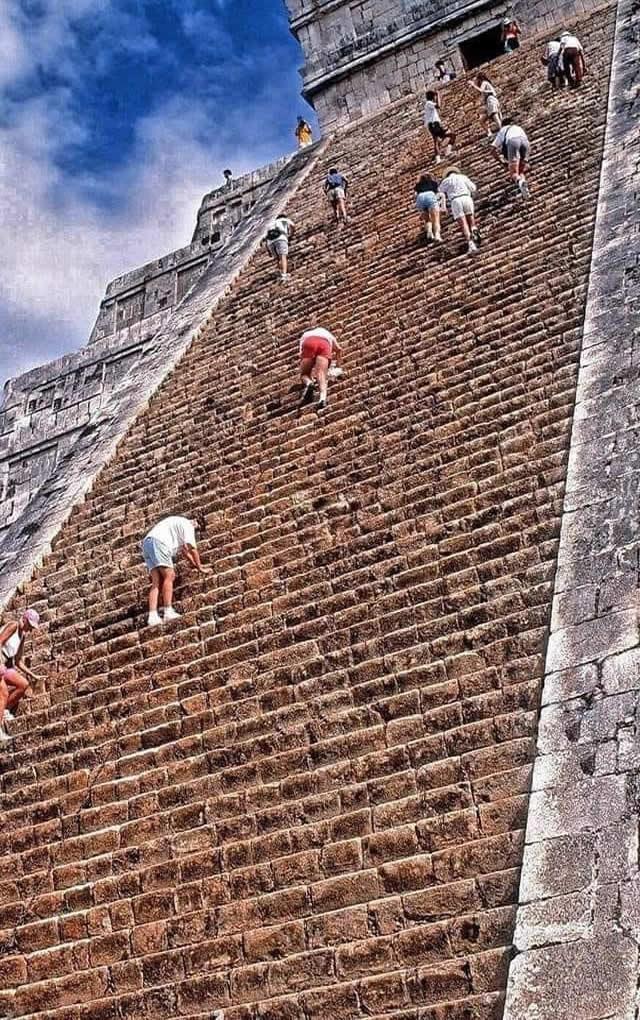
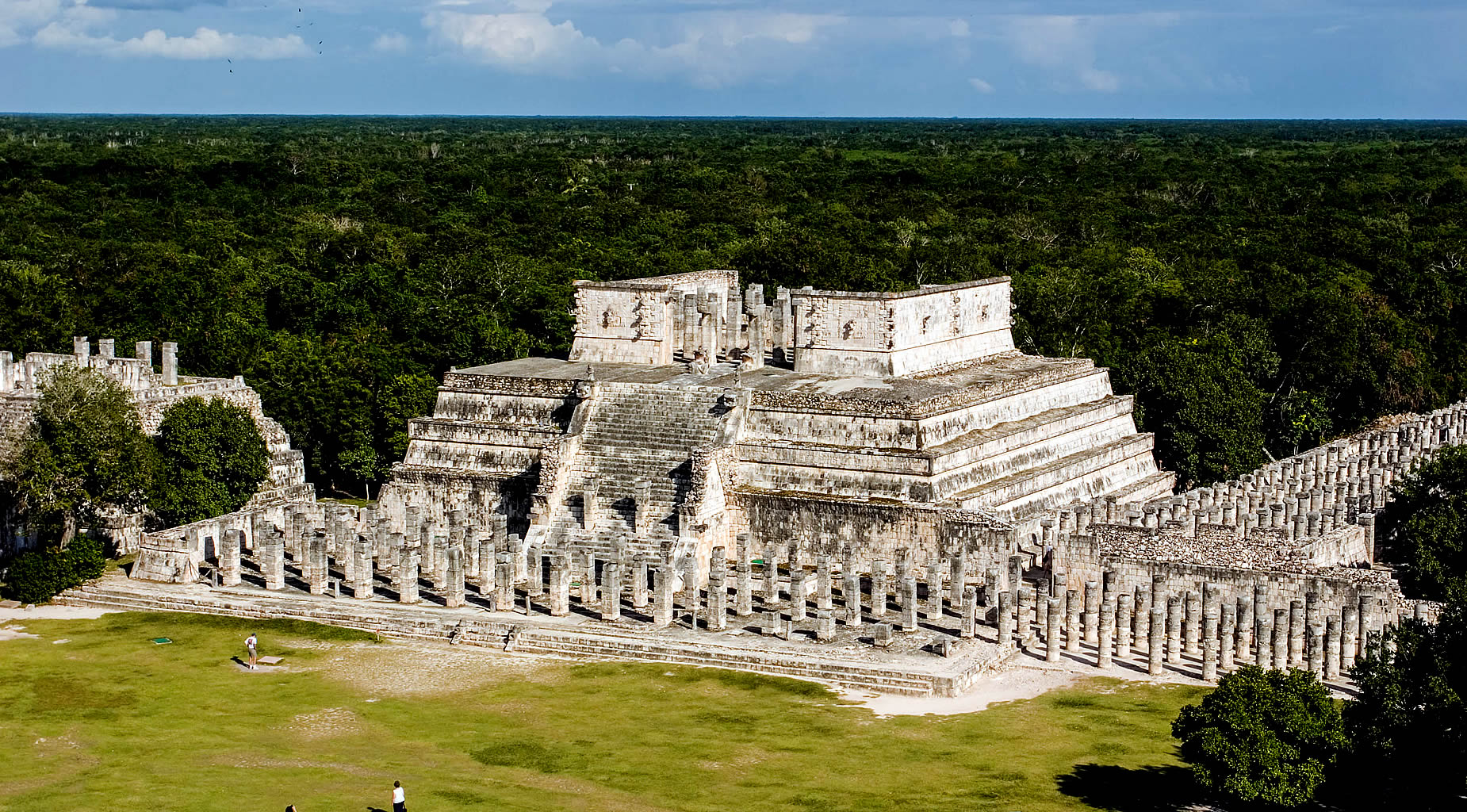
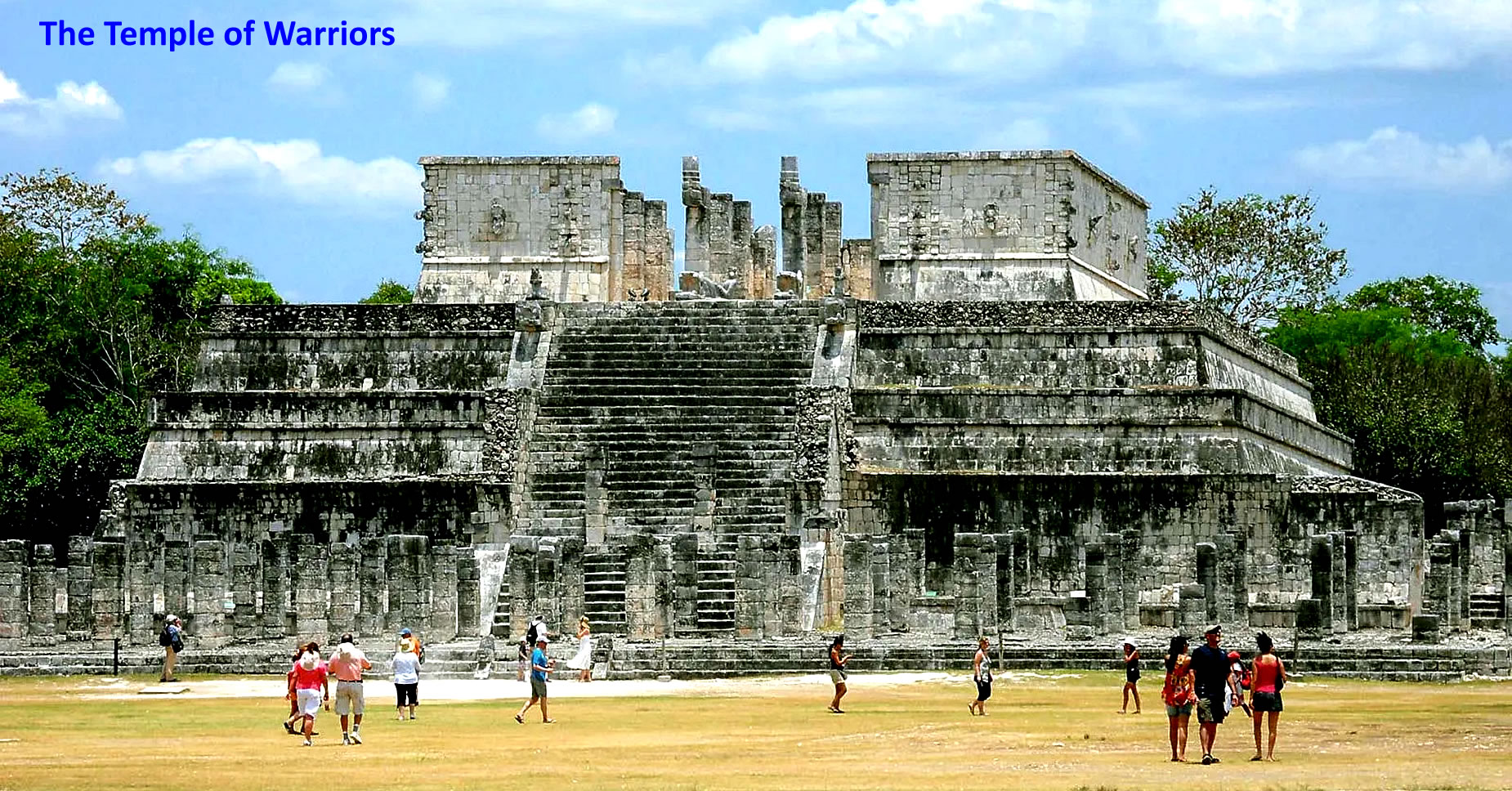
| Chichen Itza was a large pre-Columbian city built by the Maya people of the Terminal Classic period. The archeological site is located in Tinúm Municipality, Yucatán State, Mexico. Chichen Itza is one of the most visited archeological sites in Mexico with over 2.6 million tourists in 2017.
Chichen Itza was a major focal point in the Northern Maya Lowlands from the Late Classic (c. AD 600–900) through the Terminal Classic (c. AD 800–900) and into the early portion of the Postclassic period (c. AD 900–1200). The site exhibits a multitude of architectural styles, reminiscent of styles seen in central Mexico and of the Puuc and Chenes styles of the Northern Maya lowlands. The presence of central Mexican styles was once thought to have been representative of direct migration or even conquest from central Mexico, but most contemporary interpretations view the presence of these non-Maya styles more as the result of cultural diffusion. Chichen Itza was one of the largest Maya cities and it was likely to have been one of the mythical great cities, or Tollans, referred to in later Mesoamerican literature. The city may have had the most diverse population in the Maya world, a factor that could have contributed to the variety of architectural styles at the site. The ruins of Chichen Itza are federal property, and the site's stewardship is maintained by Mexico's Instituto Nacional de Antropología e Historia (National Institute of Anthropology and History). The land under the monuments had been privately owned until 29 March 2010, when it was purchased by the state of Yucatán. |
The Maya name "Chichen Itza" means "At the mouth of the well of the Itza." This derives from chi', meaning "mouth" or "edge", and chʼen or chʼeʼen, meaning "well". Itzá is the name of an ethnic-lineage group that gained political and economic dominance of the northern peninsula. One possible translation for Itza is "enchanter (or enchantment) of the water," from its (itz), "sorcerer", and ha, "water". The name is spelled Chichén Itzá in Spanish, and the accents are sometimes maintained in other languages to show that both parts of the name are stressed on their final syllable. Other references prefer the Maya orthography, Chichʼen Itzaʼ (pronounced [tʃitʃʼen itsáʔ]). This form preserves the phonemic distinction between chʼ and ch, since the base word chʼeʼen (which, however, is not stressed in Maya) begins with a postalveolar ejective affricate consonant. The word "Itzaʼ" has a high tone on the "a" followed by a glottal stop (indicated by the apostrophe).
Evidence in the Chilam Balam books indicates another, earlier name for this city prior to the arrival of the Itza hegemony in northern Yucatán. While most sources agree the first word means seven, there is considerable debate as to the correct translation of the rest. This earlier name is difficult to define because of the absence of a single standard of orthography, but it is represented variously as Uuc Yabnal ("Seven Great House"), Uuc Hab Nal ("Seven Bushy Places"), Uucyabnal ("Seven Great Rulers") or Uc Abnal ("Seven Lines of Abnal"). This name, dating to the Late Classic Period, is recorded both in the book of Chilam Balam de Chumayel and in hieroglyphic texts in the ruins. |
 |