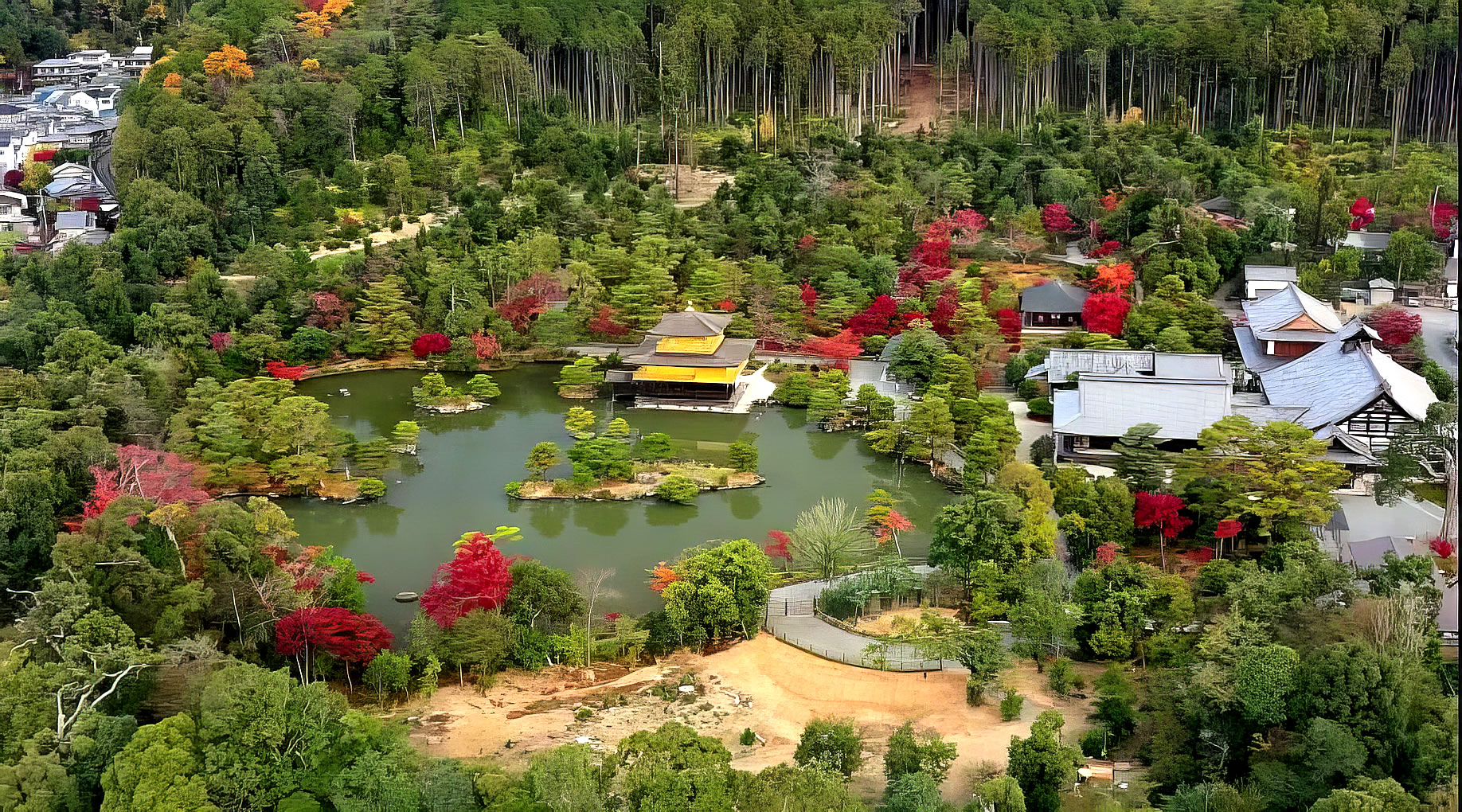
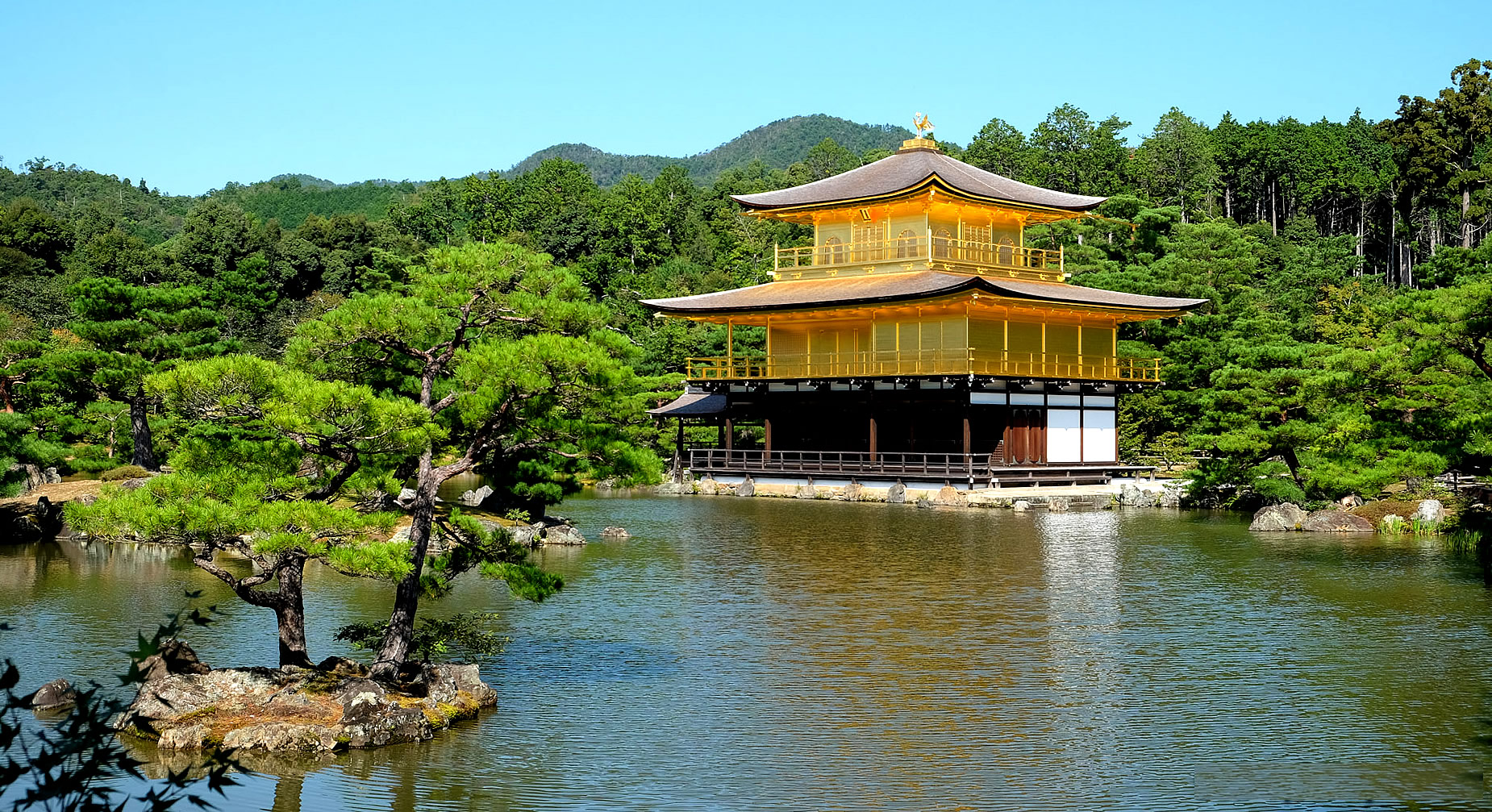
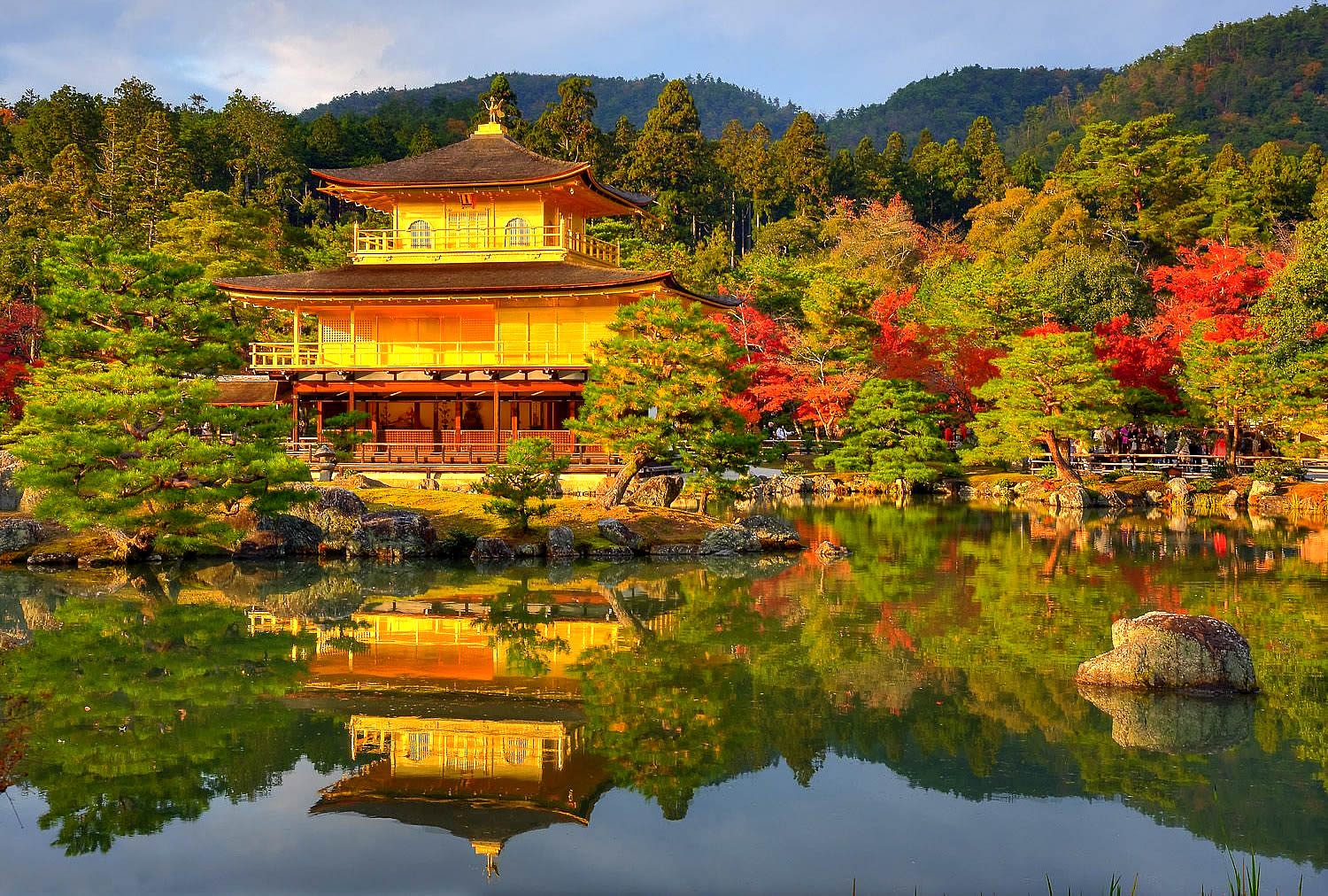
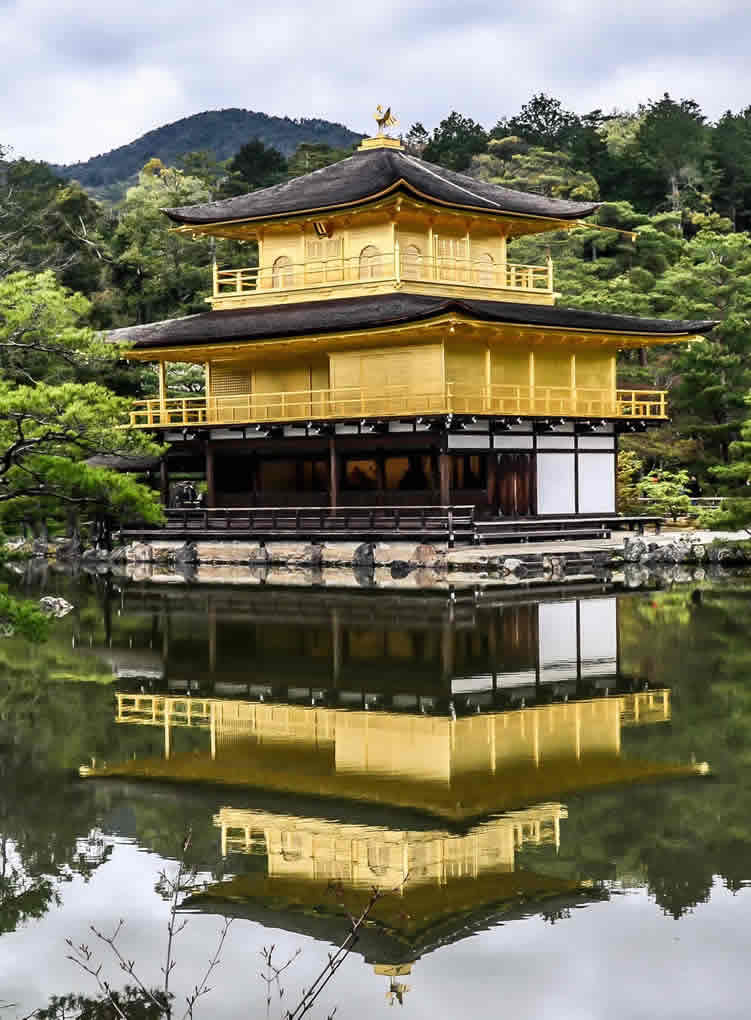
| Kinkaku-ji (金閣寺, literally "Temple of the Golden Pavilion"), officially named Rokuon-ji (鹿苑寺, literally "Deer Garden Temple"), is a Zen Buddhist temple in Kyoto, Japan. It is one of the most popular buildings in Kyoto, attracting many visitors annually. It is designated as a National Special Historic Site, a National Special Landscape and is one of 17 locations making up the Historic Monuments of Ancient Kyoto which are World Heritage Sites.
The site of Kinkaku-ji was originally a villa called Kitayama-dai (北山第), belonging to a powerful statesman, Saionji Kintsune. Kinkaku-ji's history dates to 1397, when the villa was purchased from the Saionji family by shōgun Ashikaga Yoshimitsu and transformed into the Kinkaku-ji complex.When Yoshimitsu died the building was converted into a Zen temple by his son, according to his wishes. During the Ōnin war (1467–1477), all of the buildings in the complex aside from the pavilion were burned down.
On 2 July 1950, at 2:30 am, the pavilion was burned down by a 22-year-old novice monk, Hayashi Yoken, who then attempted suicide on the Daimon-ji hill behind the building. He survived, and was subsequently taken into custody. The monk was sentenced to seven years in prison, but was released because of mental illnesses (persecution complex and schizophrenia) on 29 September 1955; he died of tuberculosis in March 1956. During the fire, the original statue of Ashikaga Yoshimitsu was lost to the flames (now restored). A fictionalized version of these events is at the center of Yukio Mishima's 1956 book The Temple of the Golden Pavilion, and another in the ballet RAkU.
|
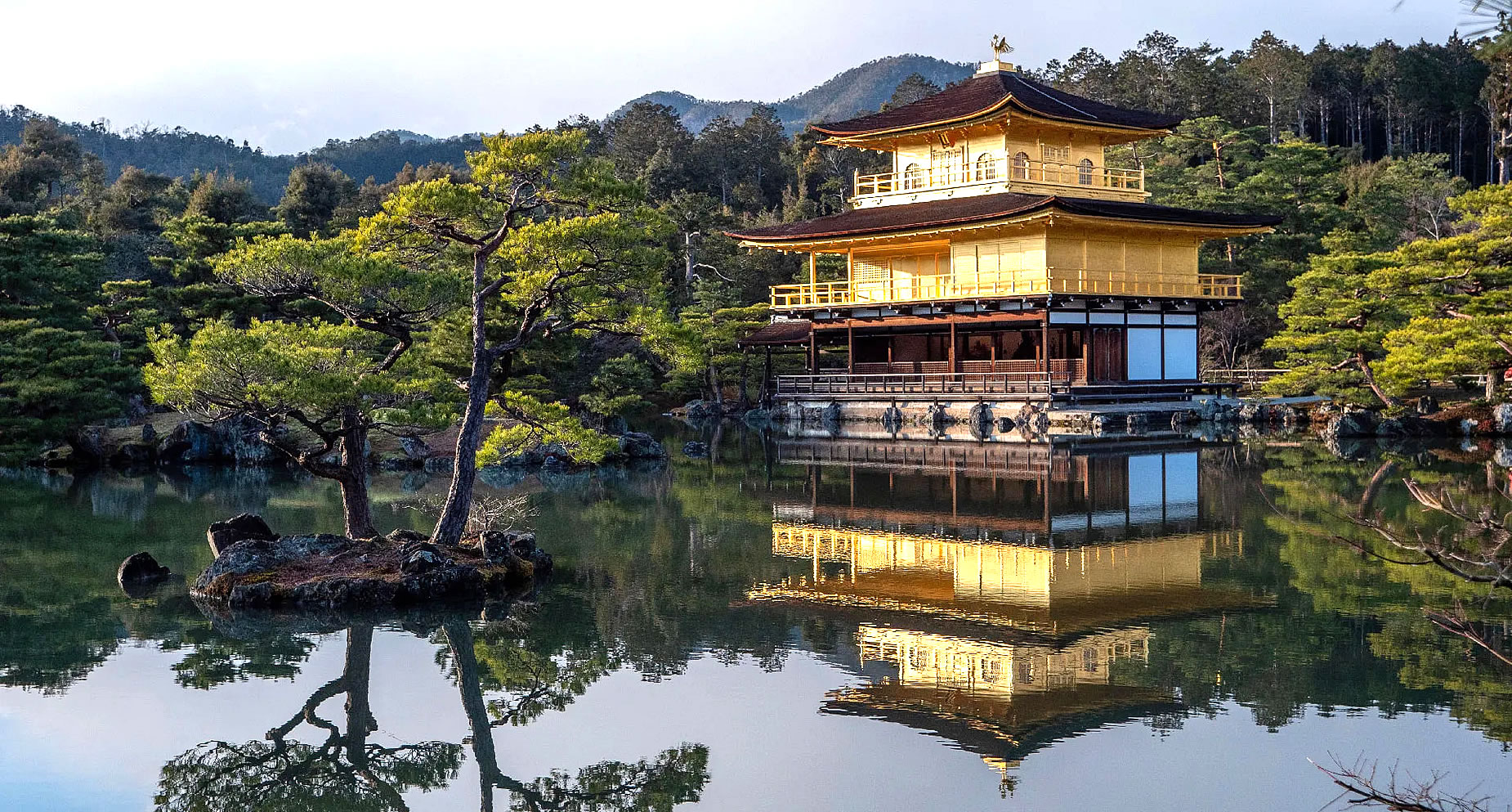
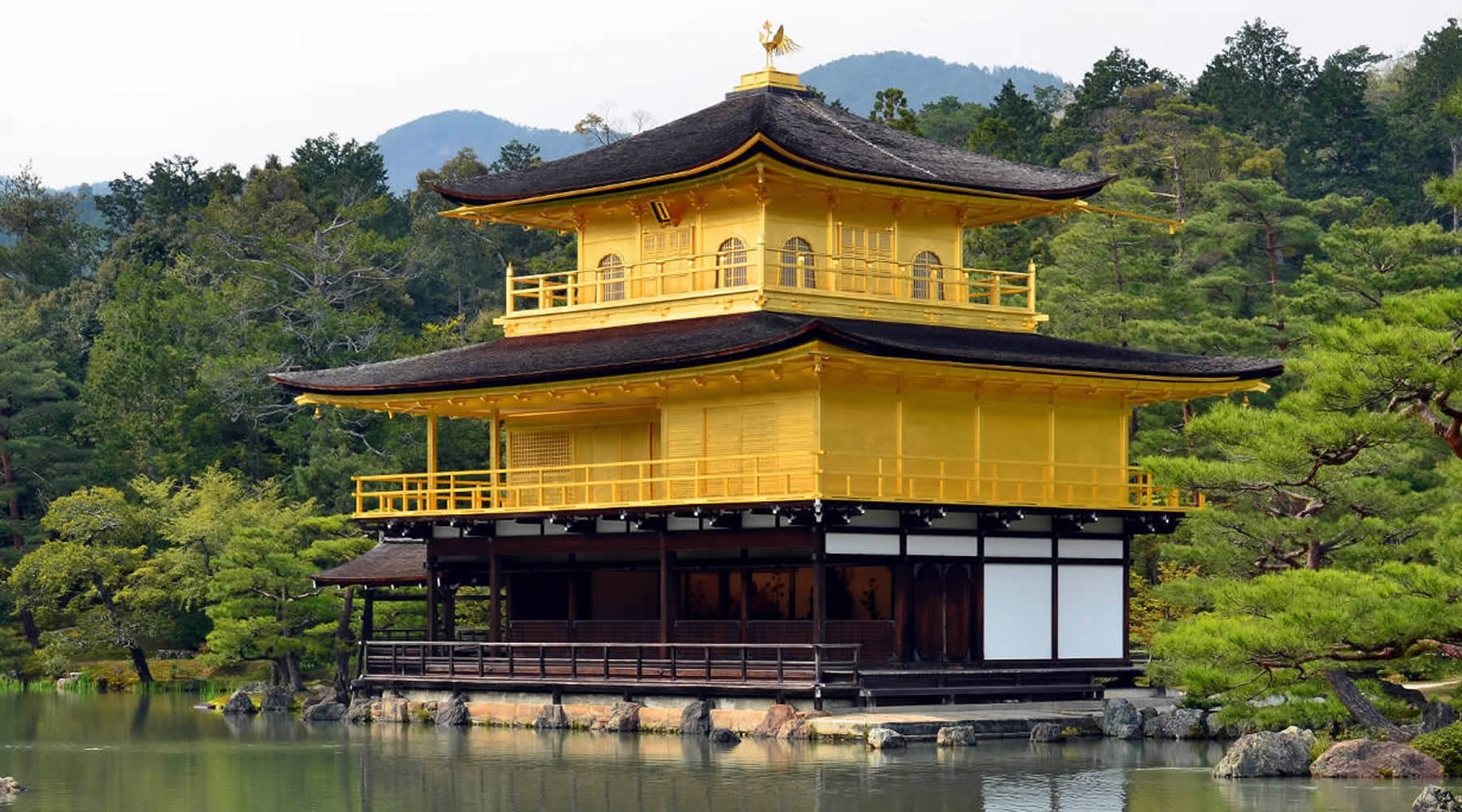
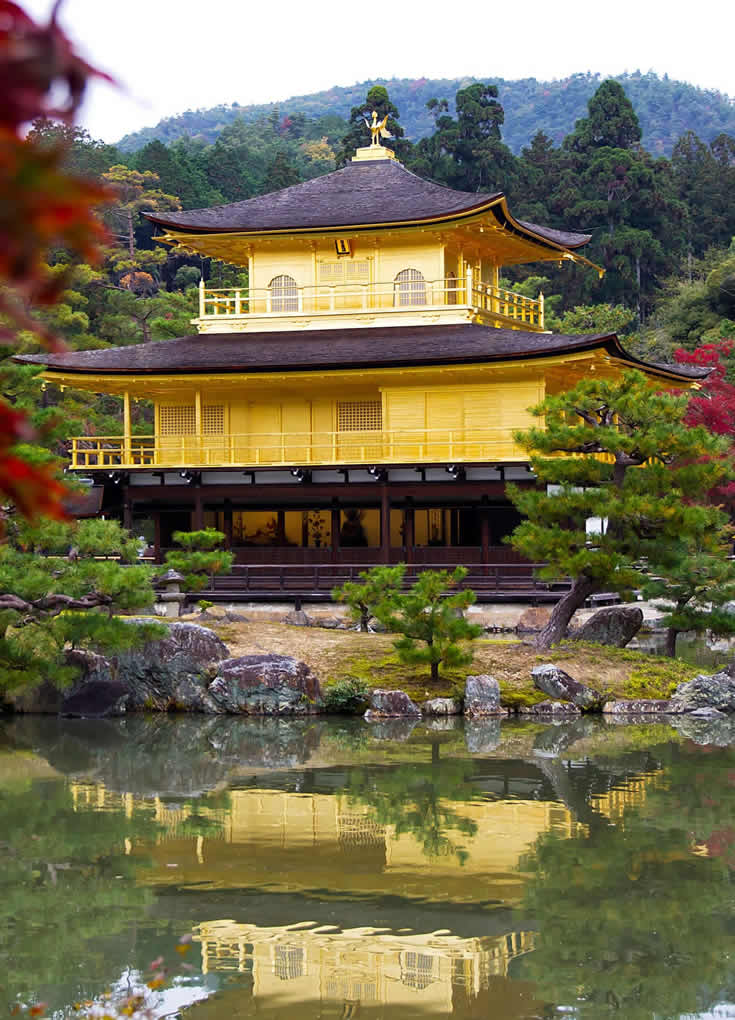
The present pavilion structure dates from 1955, when it was rebuilt. The pavilion is three stories high, 12.5 meters (40 feet) in height. The reconstruction is said to be a copy close to the original, although some doubt such an extensive gold-leaf coating was used on the original structure. In 1984, it was discovered that the gold leaf on the reconstructed building had peeled off, and from 1986 to 1987, it was replaced with 0.5 μm gold leaf, five times the thickness of the gold leaf on the reconstructed building. Although Japanese gold leaf has become thinner with the passage of time due to improved technology, the 0.5 μm gold leaf is as thick as traditional Japanese gold leaf.
Additionally, the interior of the building, including the paintings and Yoshimitsu's statue, were also restored. Finally, the roof was restored in 2003. The name Kinkaku (金閣 gold pavilion) is derived from the gold leaf that the pavilion is covered in. Gold was an important addition to the pavilion because of its underlying meaning. The gold employed was intended to mitigate and purify any pollution or negative thoughts and feelings towards death. Other than the symbolic meaning behind the gold leaf, the Muromachi period heavily relied on visual excesses. With the focus on the Golden Pavilion, the way that the structure is mainly covered in that material creates an impression that stands out because of the sunlight reflecting and the effect the reflection creates on the pond. |